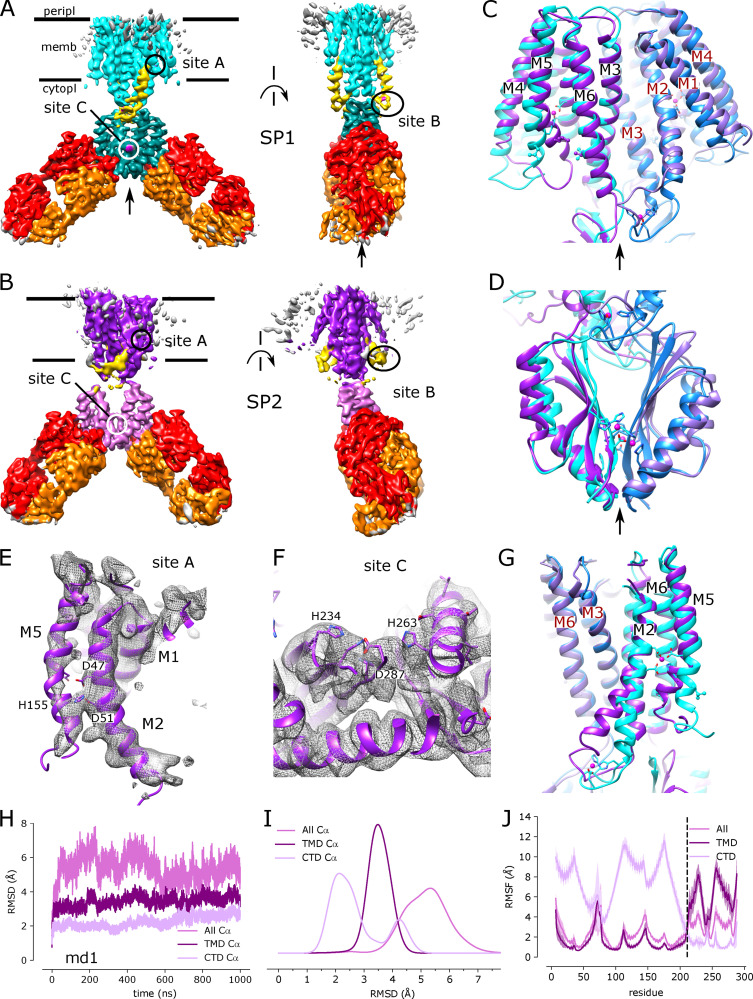
Figure 4.
Cryo-EM structure of EDTA-treated YiiP/Fab complex (SP2) and comparison with the untreated complex (SP1).(A) SP1 structure of untreated complex showing C2 symmetry (rotation axis indicated by arrow) with colors highlighting the following features: light cyan for the TMD, dark cyan for the CTD, yellow for the TM2/TM3 loop, orange for the Fab light chain, and red for the Fab heavy chain. The location of Zn sites A, B, and C are indicated by circles. (B) Comparable views of the SP2 structure for the EDTA-treated complex with the following colors: dark purple for the TMD, light purple for the CTD, and yellow for the TM2/TM3 loop. The twofold symmetry is disrupted by the bend between the CTD and TMD. (C) Alignment of TMDs for the two structures (cyan for SP1 and purple for SP2) shows preservation of the overall architecture of this domain including the dimer interface and twofold symmetry (arrow). Individual protomers are shown in different shades. (D) Alignment of the CTDs for the two structures shows preservation of the dimer interface and twofold symmetry (arrow), with a modest increase in separation in the apo state. (E) Close-up of Zn site A in the TMD from the SP2 structure showing a lack of density at the ion binding site and a bend in the M2 helix near Asp51. (F) Close-up view of Zn site C in the CTD with lack of density indicating an absence of ions at this site. (G) Comparison of M2 and M5 in apo and holo states shows bends originating at Zn site A. (H) Cα RMSD plots for one of the three MD simulations (md1) of the apo state (traces for md0 and md2 are shown in Fig. S9). The three traces correspond to the different alignment schemes as indicated in the legend and described in Fig. 3. (I) Distributions of RMSDs derived from all three simulations using the three alignment schemes. (J) RMSF profiles averaged over both protomers from all three simulations based on the different alignment schemes. Error bands indicate the SD over these six profiles. The dashed line represents the boundary between TMD and CTD.