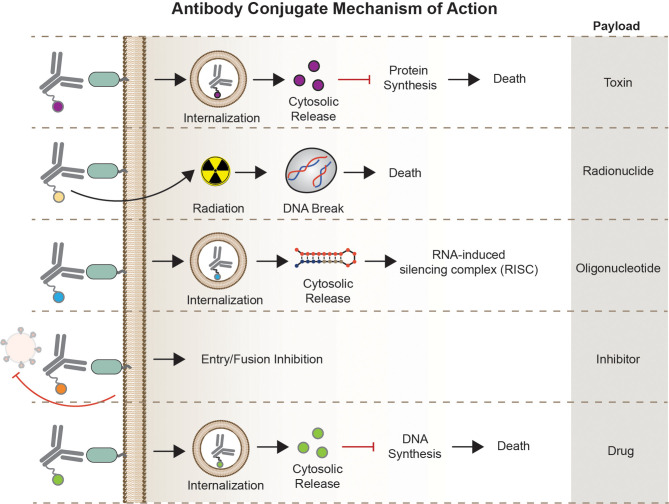
Figure 3.
Mechanism of Action. Antibody conjugates execute different mechanism of action depending on the carrier molecule, antigen, internalization requirement, and effector function of the payload. Antibody-toxin binds to target epitopes, internalized, followed by escape of toxin to the cytosol to halt protein synthesis. Antibody-radionuclide binds to the receptor to deliver ionizing radiation to the cell inducing DNA breaks. Antibody-oligonucleotide binds to its receptor, internalized, and bind complementary sequences in the cytosol for gene silencing. Antibody-drugs can act either internally or non-internally depending on the effector molecule – fusion inhibitor binds to a receptor or viral particle to inhibit entry, some classes of cytotoxic compounds act by intercalating to cell’s DNA inducing DNA/RNA synthesis.