Fig 1.
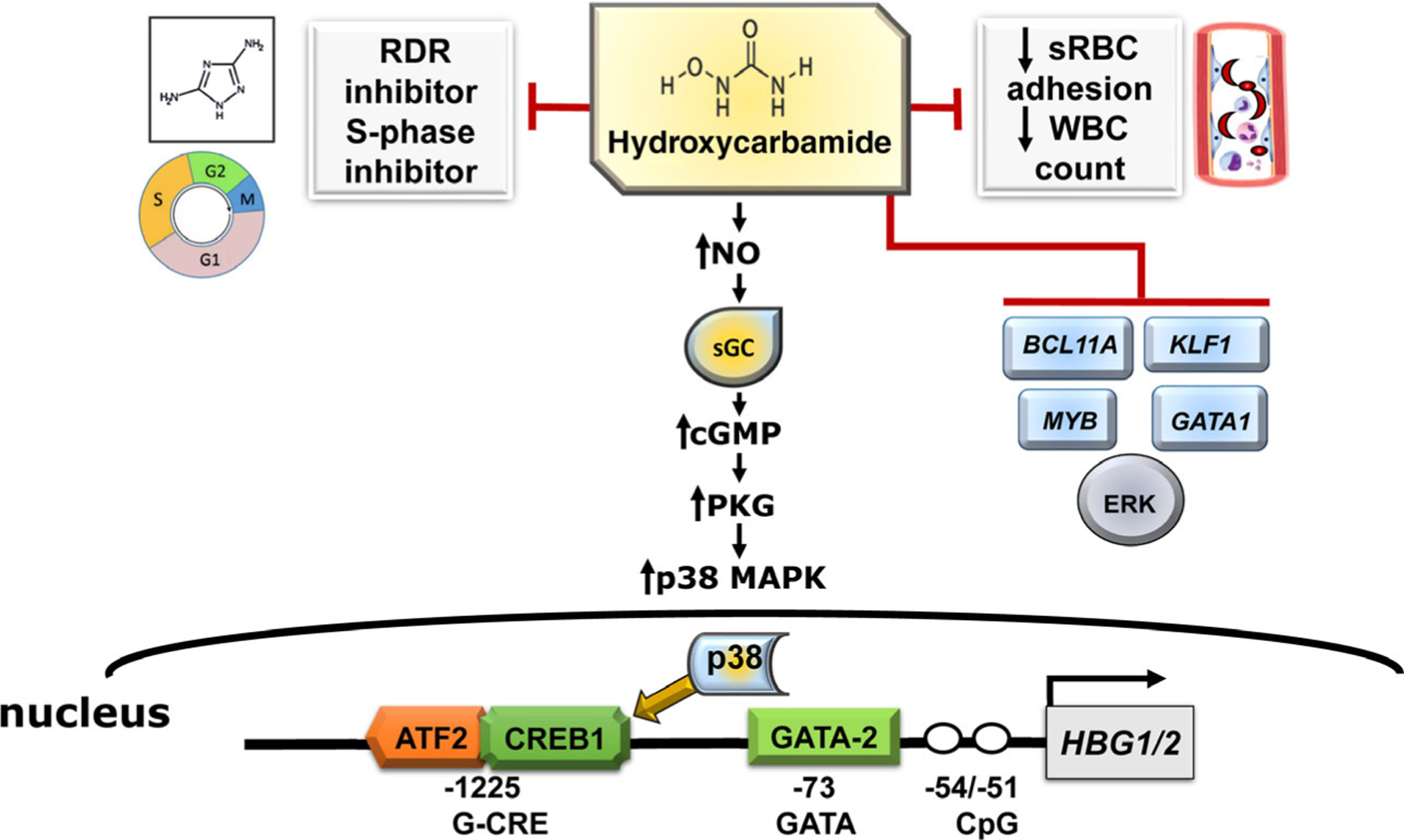
Mechanisms of fetal haemoglobin (HbF) induction by hydroxycarbamide. Shown are the various mechanisms by which hydroxycarbamide impacts the clinical symptoms of sickle cell disease. The generation of nitric oxide (NO) by hydroxycarbamide leads to sGC (soluble guanylyl cyclase) activation and subsequent cGMP-PKG signalling and p38 MAPK (mitogen-activated protein kinase) phosphorylation and repression of ERK MAPK. Once activated, p38 MAPK crosses into the nucleus and activates downstream transcription factors ATF2 and CREB1 to enhance HBG2 expression. Symbols: white circle, unmethylated cytosine. Abbreviations: ATF2, Activating Transcription Factor 2; cGMP-PKG, cyclic guanosine monophosphate-protein kinase g; CREB1, CAMP responsive element binding protein 1; ERK, extracellular signal-regulated kinase; GATA2, GATA-binding factor 2; RDR, ribonucleoside diphosphate reductase; sRBC, sickle red blood cells; WBC, white blood cell.
