Figure 2. Systemic effects and modulation of estrogens.
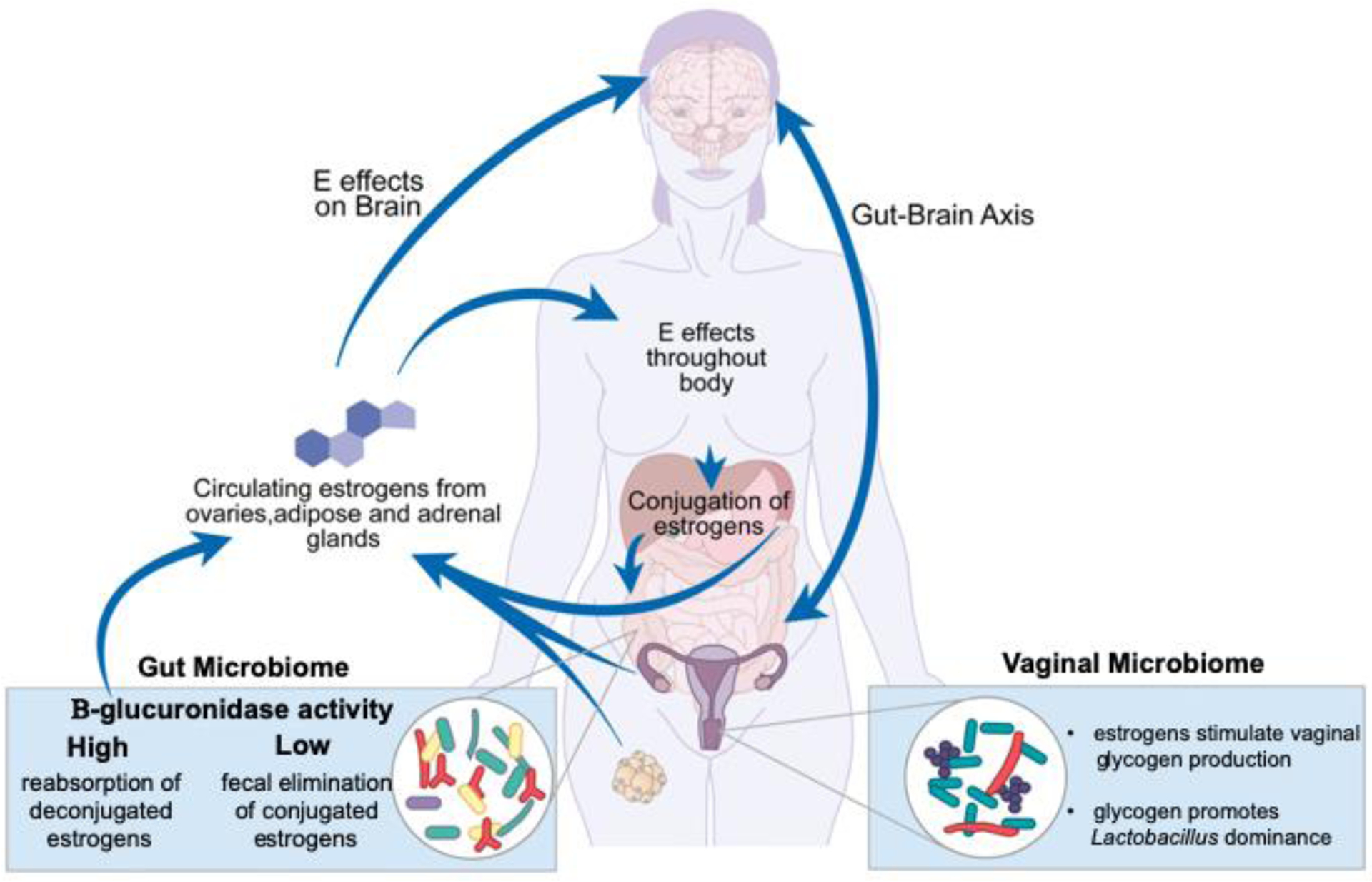
Estrogens have widespread effects throughout the body and are central to many aspects of women’s health. In addition to their central effects, estrogens act on, and are acted on, by the human microbiome. The GM consists of microbes that produce β-glucuronidase. This enzyme can deconjugate estrogens that were bound for excretion, causing them to reenter the body and remain active [7]. The VM composition is influenced by estrogens in the body via its effects on the vaginal epithelium [12]. Vaginal glycogen increases in response to estrogens and drives Lactobacillus spp. dominance in the VM [11].
