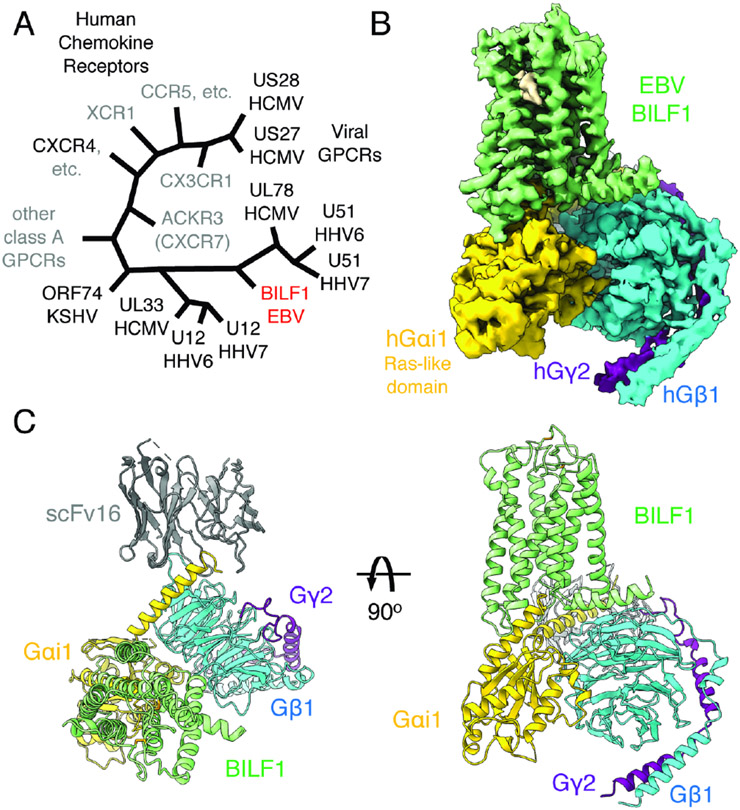
Figure 1. Cryo-EM structure of the transmembrane EBV BILF1 in complex with human Gi heterotrimer.
(A) A cartoon representation of the phylogenetic relationships between vGPCRs encoded by human herpesviruses (HHV) and human chemokine receptors. The herpesvirus strains are indicated at the bottom of the vGPCR names. The figure was modified from (Montaner et al., 2013). EBV: Epstein-Barr virus. HCMV: Human cytomegalovirus. KSHV: Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus. CCR, CXCR, CX3CR, XCR, and ACKR: CC, CXC, CX3C, XC, and atypical chemokine receptors, respectively. (B) 3.2 Å cryo-EM 3D reconstruction from the full-length EBV BILF1 in complex with human Gαi1Gβ1γ2 heterotrimer and the G protein complex stabilizing antibody scFv16. (C) Cartoon representations of the BILF1-Gαi1Gβiγ2-scFv16 model from top-down and side views. Disulfide bond-forming cysteines are displayed as sticks. In the cryo-EM map and the cartoon model, the components are colored in green (BILF1), yellow (Gαi1), cyan (Gβ1), purple (Gγ2), and gray (scFv16). The cryo-EM map is depicted around a 3 Å distance from the model built, and the contour level is set at 4.7σ. An unassigned density observed between TM6 and TM7 is not modeled but highlighted in wheat color in the map.