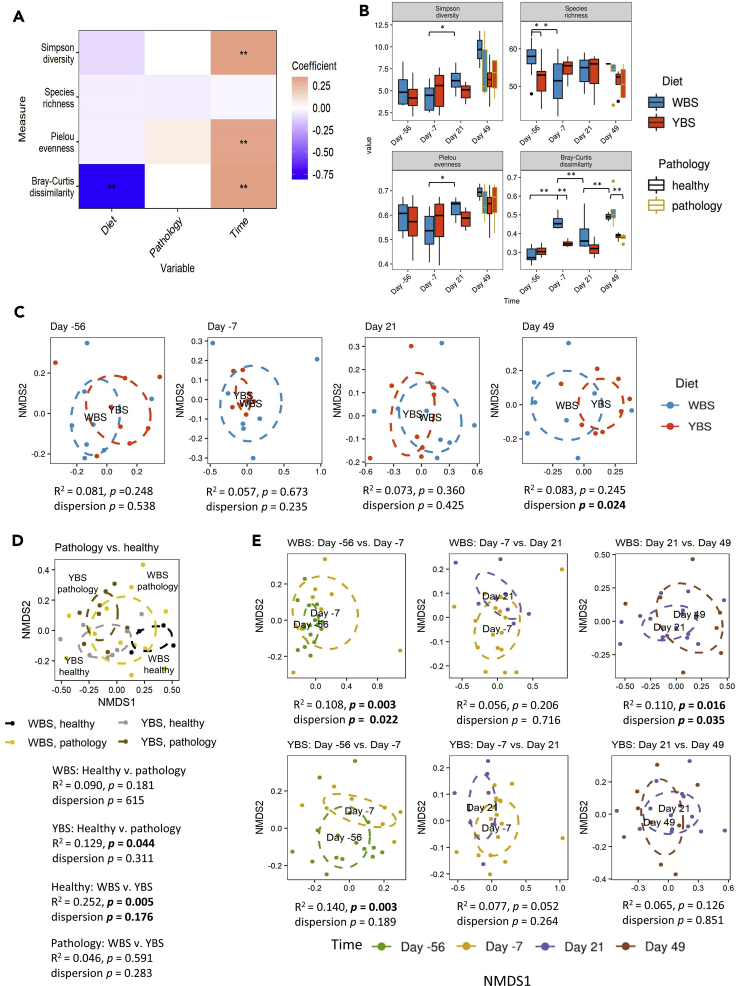
Figure 1.
Influence of diet, pathology, and time on microbiome diversity (related to Table S2)
(A) Heatmap of coefficients obtained from a mixed effect model analyses of α-diversity metrics and Bray Curtis distances. Double asterisks indicate coefficients for which the 95% confidence interval did not overlap zero.
(B) Boxplots showing various diversity metrics, including the Simpson index, species richness, Pielou evenness, and Bray-Curtis distances. An analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by Tukey's post hoc test was used to identify significantly different diversity measures between diets at each time point and within diets relative to the previous time point. Lines represent minimum and maximum values. Significance was established at p < 0.05.
(C–E) Non-metric multidimensional scaling (NMDS) plots based on the Bray-Curtis distance comparing (C) diets at each time point, (D) healthy and pathology within each diet, and (E) time points within each diet. PERMANOVA was used to determine whether two groups were significantly different, with a significance threshold of p < 0.05.