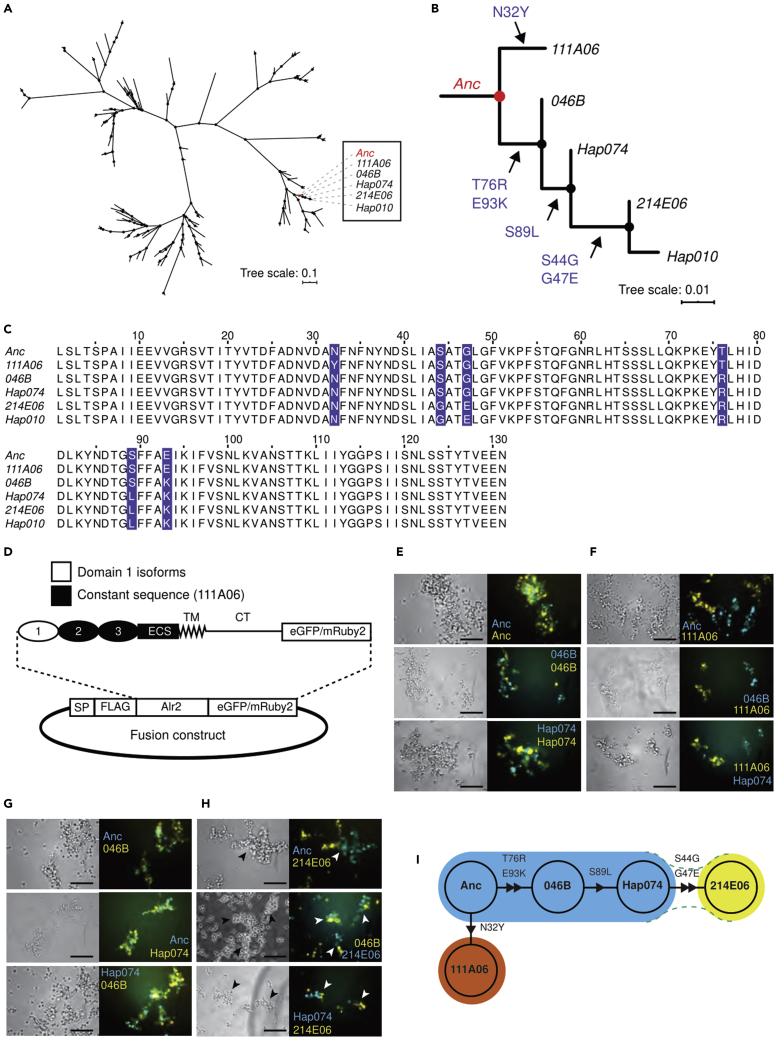
Figure 2.
Evolution of novel binding specificities via point mutation
(A) Maximum-likelihood tree of 146 domain 1 coding sequences.
(B) Expansion of clade that includes 111A06 and 214E06. Allele names on branch. Amino acid changes indicated along branches.
(C) Multiple sequence alignment of clade. Variant residues highlighted.
(D) Plasmid map Alr2 fusion proteins. (E-H) Representative images of cell aggregation assays.
(E) Anc, 046B, and Hap074 against themselves.
(F) Anc, 046B, and Hap074 against 111A06.
(G) All pairwise combinations of Anc, 046B, and Hap074.
(H) Anc, 046B, and Hap074 versus 214E06. Arrowheads point to semi-mixed aggregates (See also Figure S1). Scale bar = 100 μm.
(I) Node network of isoforms colored by binding specificity. Triangles indicate the hypothesized direction of mutation from Anc. Green dotted lines indicate weaker heterophilic interactions.