Figure 2.
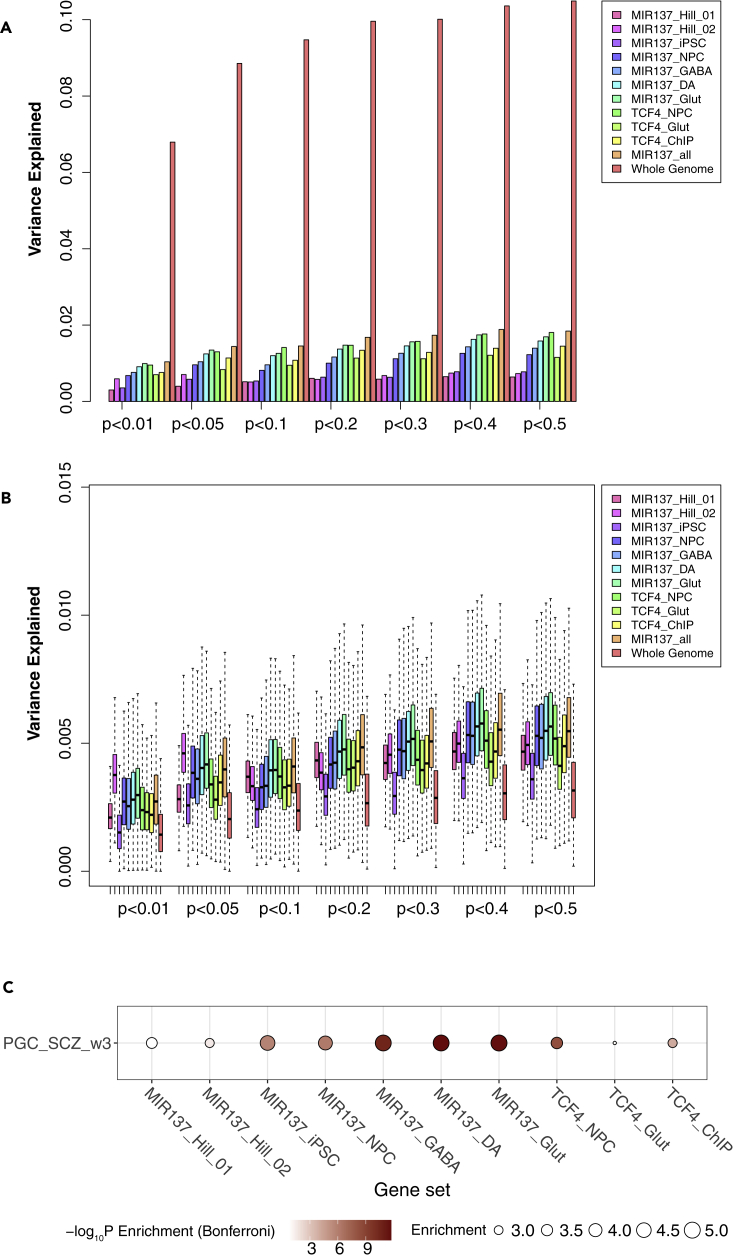
PRS analysis of different lists of target genes of MIR137 and TCF4 annotated in a 20-kb window for the MGS sample
Gene sets in (A) and (B) were described in Table 1.
(A) PRS result using LD-pruned SNPs (r2 < 0.2) for each gene list. The variance explained in the target sample is based on risk scores derived from an aggregated sum of weighted SNP risk allele effect sizes estimated from the discovery samples at seven significance thresholds (p < 0.01, 0.05, 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, and 0.5). The y axis indicates the percentage of phenotypic variance explained by the PRS (Nagelkerke's pseudo R2).
(B) The permutation (N = 1,000) PRS results based on randomly selected 1,500 SNPs for each gene set. Data are presented as mean ± SEM.
(C) Stratified LDSC analysis showing stronger enrichment of SZ GWAS SNP heritability in neural MIR137-target gene sets. Shown are the folds of enrichment of SNP heritability (proportion of explained heritability h2 normalized by the proportion of SNPs in each gene set) and the statistical significance (Bonferroni-corrected p values; in -log10 scale).