Figure 4.
SZ PRS explained by MIR137 target genes (in Figure 2) is mainly attributed to a small number of neuron-specific genes
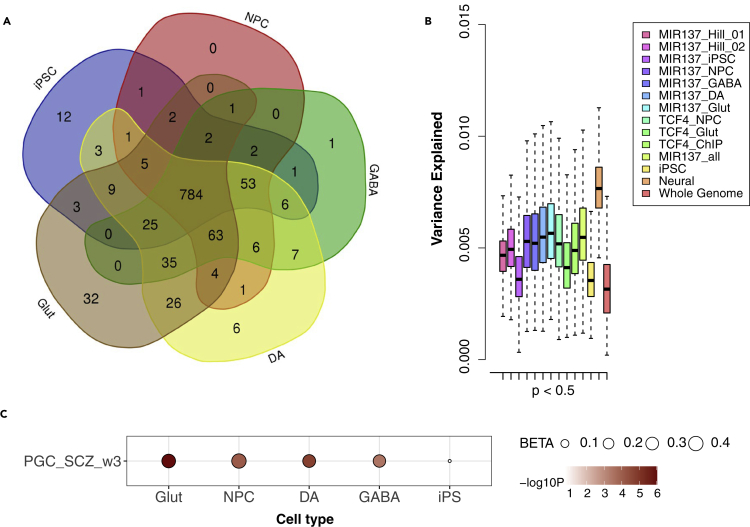
(A) Venn diagram of the five lists of MIR137 target genes expressed in different cell types derived from hiPSC. NPC, neuron progenitor cells; GABA, GABAergic neurons; DA, dopaminergic neurons; Glut, glutamatergic neurons.
(B) The PRS results from permutation (N = 1,000) for the small subset of MIR137 target genes expressed only in neuronal cell type (N = 182, denoted as “Neural”) or shared with hiPSC (N = 784, denoted as “iPSC”), using randomly selected 1,500 SNPs for each gene set at GWAS p-value threshold of <0.05. Data are represented as mean ± SEM.
(C) H-MAGMA analysis showing enrichment of SZ risk (PGC_wave3) in MIR137 target genes specific to each neuronal cell type but not in genes shared with iPSC (n = 784 from A). Shown in bubble plot are corresponding effect size (BETA) and enriched p-value (Bonferroni corrected; in -log10 scale) of each gene set.