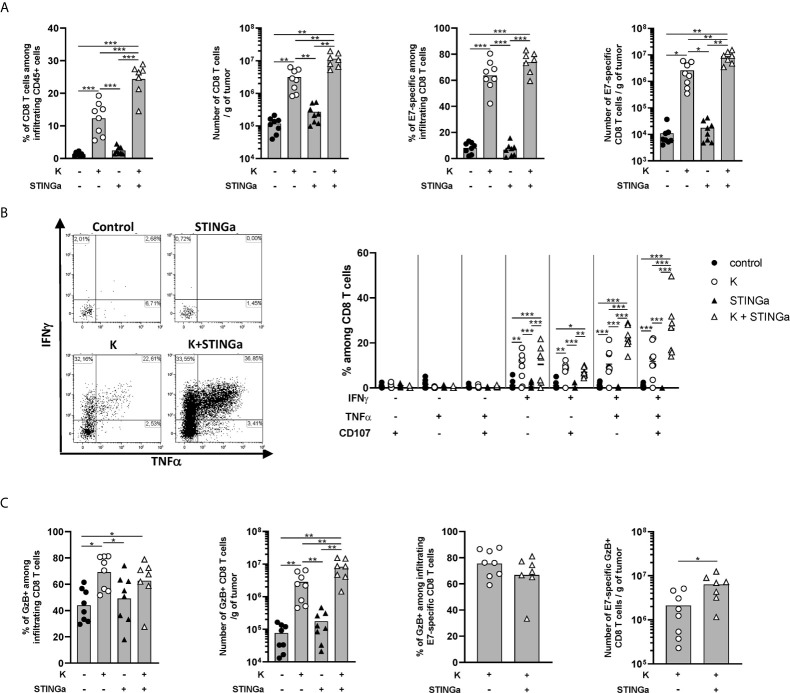
Figure 4.
Combining protein vaccine treatment with STING agonist enhances functionality of intra-tumoral CD8 T cells in TC-1 model. 105 TC-1 cells were implanted subcutaneously on the back of C57BL/6 mice. When tumors were visible, mice were treated with two administrations of KISIMA vaccine, STING agonist or a combination of the two at one-week interval. One week after the last treatment, mice were sacrificed, tumor harvested, and CD8 T cells’ presence and phenotype were analyzed by flow cytometry. (A) Frequency and number of total and RAHYNIVTF (E7)-specific CD8 T cells among tumor infiltrating leukocytes. (B) Tumor infiltrating CD45+ cells were stimulated ex vivo with RAHYNIVTF peptide in the presence of Golgi inhibitor. Antigen-specific cytokine production was measured by intracellular staining; representative FACS plots and frequency of cytokine-producing among CD8 T cells are shown. (C) CD45+ tumor infiltrating cells were cultured ex vivo with Golgi inhibitor and granzyme B production was monitored by intracellular staining. Frequency and total number of granzyme B-producing total and RAHYNIVTF-specific CD8 T cells are shown. (A–C) A pool of two experiments is shown (n ≥7/group), Mann–Whitney test, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.