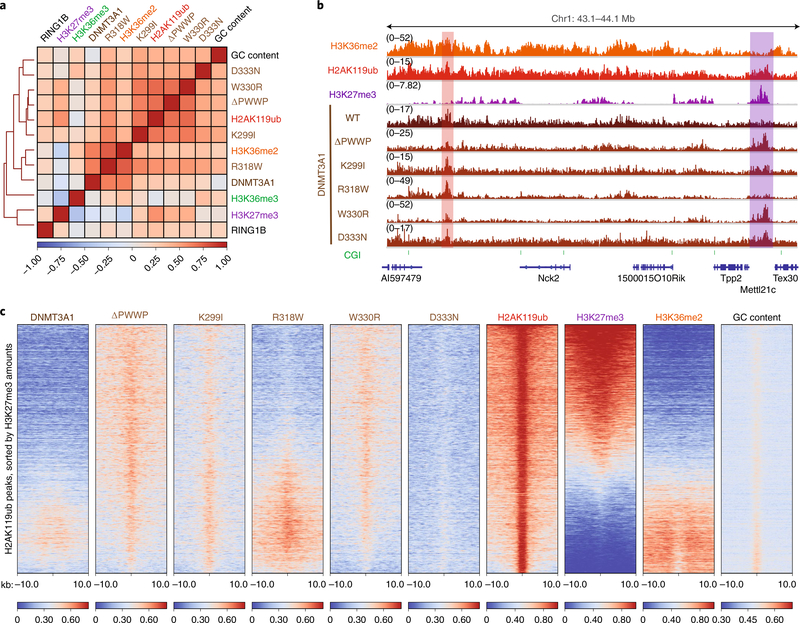
Fig. 1 |. Disease-associated mutations promote DNMT3A colocalization with H2AK119ub due to loss of PWWP domain reader functionality.
a, Heat map showing genome-wide, pairwise Pearson correlations across 10-kb bins (n = 245,842) for H3K36me2, H3K36me3, H3K27me3, H2AK119ub, GC content, DNMT3A1 wild type, DNMT3A1 PWWP mutants and RING1B. b, Genome browser representation of ChIP-seq normalized reads for H3K36me2, H2AK119ub, H3K27me3, DNMT3A1 wild type and DNMT3A1 PWWP mutants in mouse MSCs at chromosome 1: 43.1–44.1 Mb. Genes from the RefSeq database are annotated at the bottom. The shaded areas indicate H2AK119ub-enriched genomic regions associated with H3K27me3 (purple) and H3K36me2 (red). c, Enrichment heat map depicting ChIP-seq normalized reads centered at H2AK119ub peaks ±10 kb (n = 16,064), sorted by H3K27me3 amounts for DNMT3A1 wild type, DNMT3A1 PWWP mutants, H2AK119ub, H3K27me3, H3K36me2 and GC content.