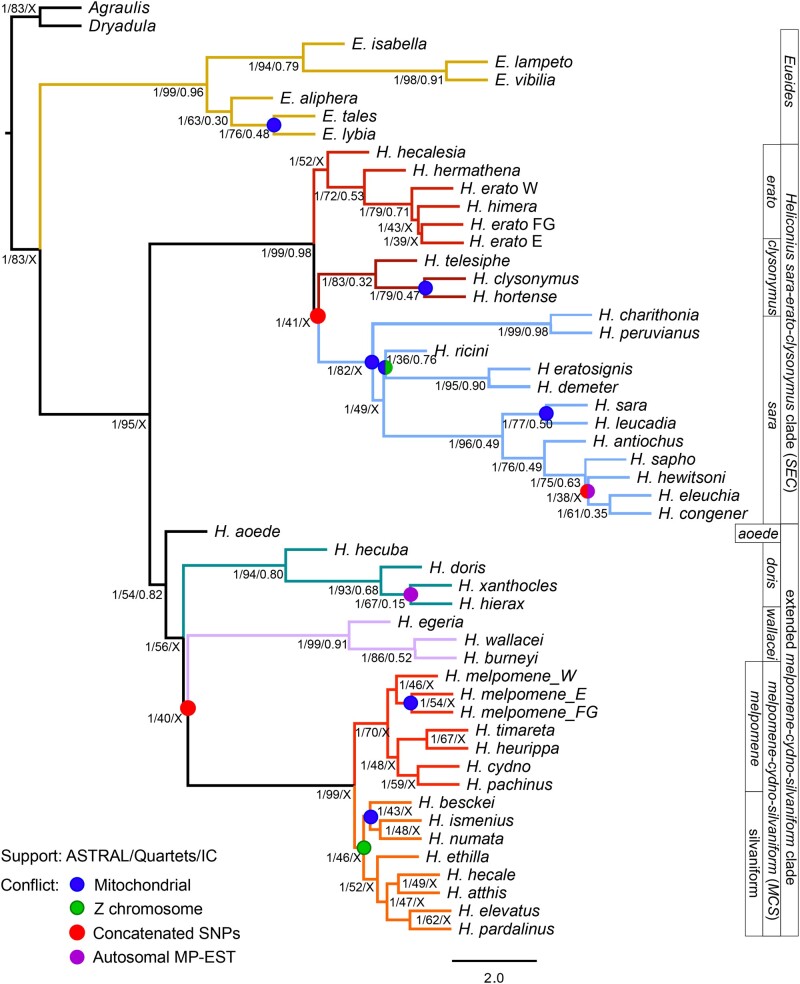
Fig. 1.
Bifurcating model of Heliconiini phylogeny obscures the underlying incongruence. The topology was inferred by the multispecies coalescent method ASTRAL-III from 6,725 orthologous autosomal genes. All nodes, except for the CHT clade are supported in 100% bootstrap replicates. In addition, three types of support values are presented: ASTRAL branch support for a quadripartition (on a 0–1 scale); percentage of quartets in individual gene trees containing a specific node; and the Internode Certainty measure of gene tree incongruence (0–1 scale; X indicates the node is not found in the consensus). Colored circles indicate conflict between the topology of the ASTRAL autosomal tree, and the estimates from: mitochondrial data under ML (blue); sex-linked genes (Z chromosome) in ASTRAL (green); concatenated SNPs under ML (red); the alternative coalescent method MP-EST (violet). Branch lengths are in coalescent units, and arbitrarily set to 1.0 for the terminal branches. Branch colors correspond to previously defined clades (Kozak et al. 2015): red—Heliconius melpomene/cydno; orange—silvaniforms (MCS); violet—Heliconius wallacei; green—Heliconius doris; blue—Heliconius sara; crimson—Heliconius clysonymus; scarlet—Heliconius erato; brown—Eueides.