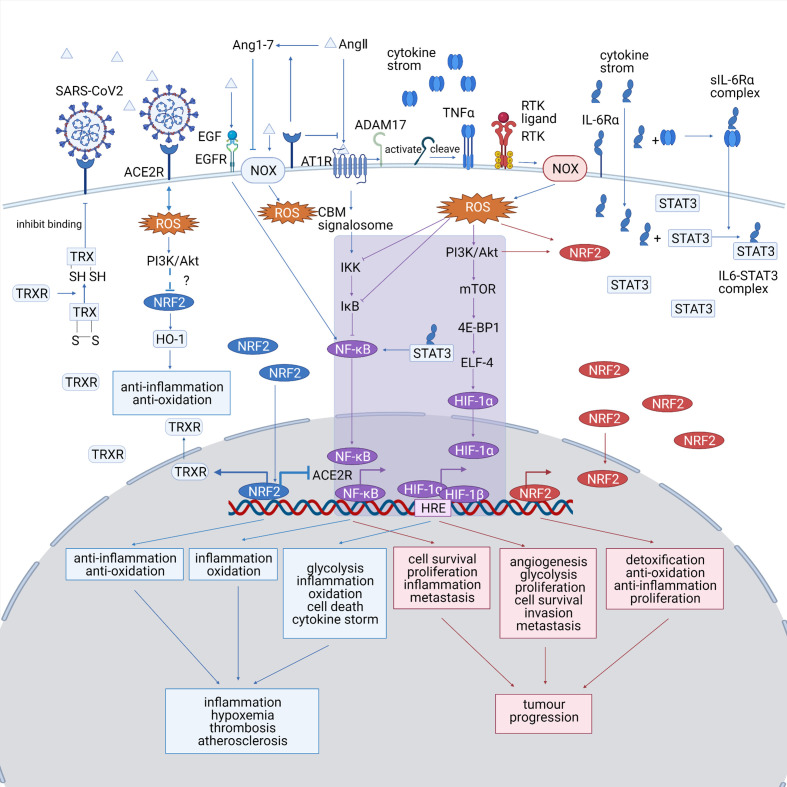
Figure 2.
(Created with BioRender.com). A summary of the ROS-associated signaling pathways in both diseases. The COVID-19-specific pathways are marked in blue, the lung cancer-specific pathways are shown are marked in red, and the common pathways shared by both diseases are marked in purple. NRF2, HIF-1, and Nf-κB pathways play significant roles in both COVID-19 and lung cancer and probably bridges the mutual impact between them. HIF-1 and Nf-κB pathway, which are typical ROS-associated pathways, are activated in both diseases, which promote inflammation and tumor progression. The altered NRF2 pathway show opposite trends between the diseases, as it is downregulated in COVID-19, making the cells less resistant to oxidative stress, while upregulated in lung cancer, promoting the proliferation of cancer cell. NOX, NADPH oxidase; ACE2R, angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 receptor; EGF, epidermal growth factor; EGFR, epidermal growth factor receptor; Ang 1–7, angiotensin 1–7; AngII, angiotensin II; AT1R, angiotensinII type 1 receptor; TNFα, tumor necrosis factor α; IL-6, interleukin 6; STAT3, signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; ROS, reactive oxygen species; TRX, thioredoxin; HO-1, heme oxygenase-1; TRXR, TRX reductase; CBM signalosome, CARD11-BCL10-MALT1 CBM signalosome; IKK, IκB-kinase; PI3K, phosphatidyl inositol 3-kinase; Akt, protein kinase B; mTOR, mammalian target of rapamycin; 4E-BP1, eIF4E-binding protein; ELF4, E74 like ETS transcription factor 4; HRE, hypoxia-responsive element.