Figure 1.
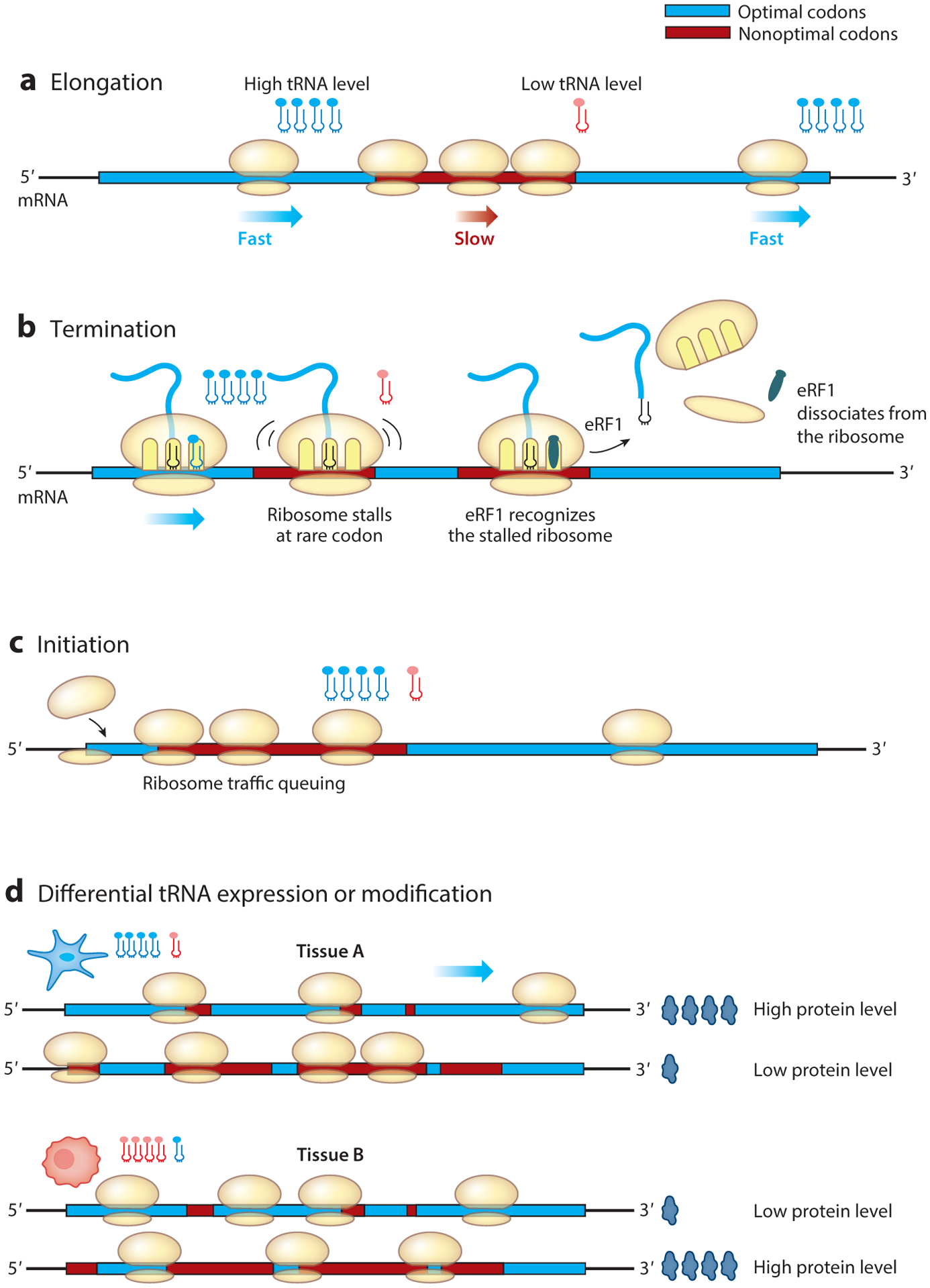
(a) Codon usage affects the speed of translation elongation: Optimal codons (light blue) speed up elongation, while nonoptimal codons (red) slow it down. (b) Codon usage regulates translation efficiency by affecting premature translation termination. Nonoptimal codons result in the ribosome stalling with an empty A-site, which can be recognized by the termination factor eRF1 to trigger premature termination. (c) Rare codon clusters downstream of the start codon can result in ribosome queuing, which may inhibit translation initiation. (d) Differential tRNA expression or modification levels in different cell types can result in the presence of different tRNA pools, influencing the cell type–specific translation of mRNAs.
