Figure 2.
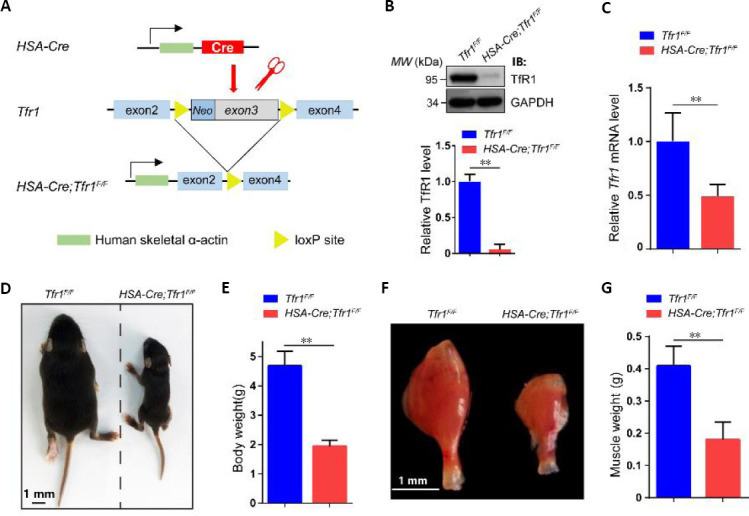
Generation of HSA-Cre;Tfr1F/F cKO mice and characterization of phenotypes.
(A) Schematic of the generation of HSA-Cre;Tfr1F/F cKO mice. The HSA-Cre transgene expressed in skeletal muscle was used to recombine loxP sites flanking Tfr1 exons 3 to generate HSA-Cre;Tfr1F/F cKO mice. (B) Representative western blot showing the expression of TfR1 in skeletal muscles from P7 Tfr1F/F control and HSA-Cre;Tfr1F/F mutants. Quantitative analysis of western blots reveals significantly decreased expression of TfR1 in mutants compared with control littermates. (C) Quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction analysis indicates significantly decreased expression of the Tfr1 gene in mutants compared with control littermates. (D) The body size of HSA-Cre;Tfr1F/F mutant mice was significantly reduced compared with the control littermates at P10. (E) Quantification of the body weight shows significant reduction in HSA-Cre;Tfr1F/F mutants compared with control littermates at P10. (F) The size of the gastrocnemius muscle in HSA-Cre;Tfr1F/F mutants was significantly smaller than that in control littermates at P10. Scale bars: 1 mm in D and F. (G) Quantification of the gastrocnemius muscle weight shows significant reduction in HSA-Cre;Tfr1F/F mutants compared with control littermates at P10. Data are expressed as the mean ± SEM (n = 4 in B, C, 10 in E, G). **P < 0.01 (Student’s t-test). cKO: Conditional knockout; GAPDH: glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase; HSA: skeletal muscle actin; P7 or P10: postnatal day 7 or 10; Tfr1: transferrin receptor 1.
