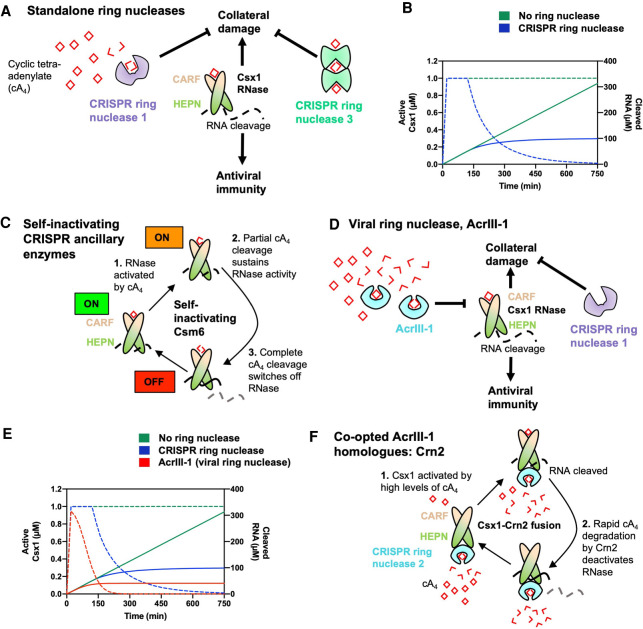
FIGURE 3.
Ring nucleases regulate the type III CRISPR immune response. (A) Cyclic tetra-adenylate (cA4)-activated Csx1 ribonucleases cleave RNA nonspecifically, which provides antiviral immunity but also causes collateral damage to cells. cA4 binds the CRISPR-associated Rossmann fold (CARF) domain of Csx1 and allosterically activates its higher eukaryotes and prokaryotes nucleotide-binding (HEPN) domain, which cleaves RNA. CRISPR ring nucleases 1 and 3 eliminate extant cA4 and deactivate Csx1, mitigating sustained collateral damage to cells. (B) Graph depicting kinetic modeling of the type III CRISPR response in a cell where 60 µM of cA4 is generated upon infection, representative of a medium-level infection. In the absence of ring nucleases, Csx1 remains in an active state (dotted green line, corresponding to left-hand side y-axis) and RNA cleavage (solid green line, corresponding to right-hand side y-axis) continues unimpeded. Csx1 is slowly deactivated when CRISPR ring nuclease 1 is present (dotted blue line) and thus RNA cleavage is limited (solid blue line). Simulations were carried out using KinTek Global Kinetic Explorer software (Johnson et al. 2009), using a previously published model of the S. solfataricus type III CRISPR defense pathway (Athukoralage et al. 2020a), and data were plotted using GraphPad Prism. (C) Some Csm6 enzymes act as bifunctional ribonucleases and ring nucleases. These enzymes cleave cA4 at the CARF domain upon cA4 binding and activating the HEPN RNase. Some Csm6 enzymes also cleave cOA at the HEPN domain. (D) Prokaryotic viruses encode an anti-CRISPR viral ring nuclease (AcrIII-1). AcrIII-1 rapidly degrades cA4 and attenuates RNA cleavage by swiftly deactivating Csx1. (E) Graph depicting the effect of having no ring nuclease (green), a host cell CRISPR ring nuclease 1 (blue), and both CRISPR ring nuclease 1 and AcrIII-1 on the active form of Csx1 (dotted lines, left-hand side y-axis) and consequent RNA cleavage (solid lines, right-hand side y-axis). When AcrIII-1 is present, Csx1 is deactivated much more quickly. (F) In some bacteria, AcrIII-1 homologs are found associated with type III CRISPR systems and these proteins have been named CRISPR ring nuclease 2 (Crn2). In Marinitoga piezophile, Csx1 is fused to Crn2, which limits Csx1 activity by rapidly and constitutively degrading cA4. The Crn2 domain only permits Csx1 activation when a high cA4 threshold, determined by the balance between cA4 affinity of the CARF domain of Csx1 and the high cA4 affinity and rate of degradation by Crn2, is reached.