FIGURE 2.
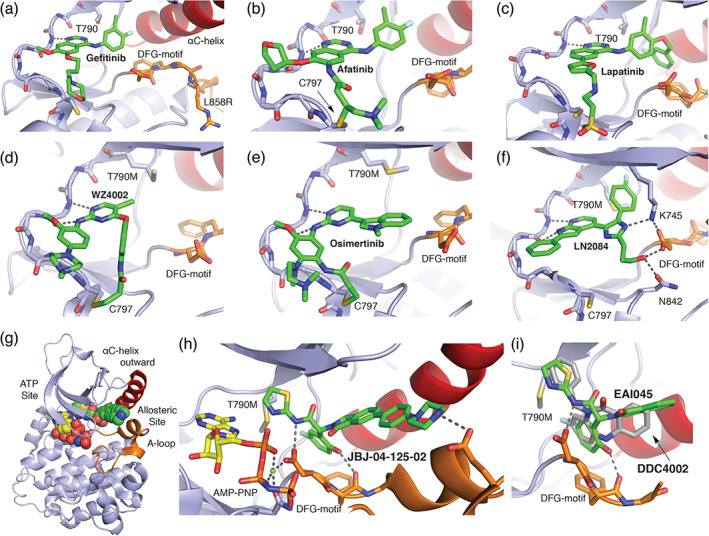
The diverse binding modes of EGFR inhibitors. (a) 1 Gefitinib co‐crystal structure with L858R EGFR (PDB ID 2ITZ). 29 For anilinoquinazoline inhibitors such as gefitinib, afatinib (b), and lapatinib (c), the quinazoline group hydrogen bonds with the “hinge” region of the kinase (dashed lines) and the aniline substituent extends into a hydrophobic pocket at the back of the ATP‐site. (b) 3 Afatinib co‐crystal structure with WT EGFR (PDB ID 4G5J). 32 Afatinib incorporates an acrylamide Michael acceptor that forms a covalent bond with C797 at the edge of the ATP‐site. (c) 4 Lapatinib co‐crystal structure PDB 1XKK. 33 Lapatinib is a “Type 1.5” inhibitor; the fluoro‐benzyl extension on the right‐hand side of the molecule enforces an inactive, C‐helix‐out conformation of the kinase. (d) 5 WZ4002 in complex with T790M EGFR (PDB ID 3IKA). 34 Anilinopyrimidine inhibitors WZ4002 and osimertinib (e) form dual hydrogen bonds with the kinase hinge (dashed lines), and both contain an acrylamide positioned to form a covalent bond with C797. (e) 6 Osimertinib co‐crystal structure with T790M EGFR (PDB ID 6JX0). 35 Note the alternate location of the acrylamide substituent as compared with WZ4002, which nevertheless takes a trajectory that allows formation of a covalent bond with C797. (f) 7 LN2084 in complex with T790M/V948R EGFR PDB ID 6V5N. 36 (g) Co‐crystal structure of T790M/V948R EGFR with allosteric inhibitor 9 JBJ‐04‐125‐02, and (h) zoom in on allosteric inhibitor binding mode PDB ID 6DUK. 37 The allosteric inhibitor occupies a pocket adjacent to, but separate from the ATP‐site. (i) Overlay of binding modes of allosteric inhibitors 8 EAI045 (PDB ID 6P1L) and 10 DDC4002 (PDB ID 6P1D). 38 Note that despite their dissimilar chemical structures, the compounds exhibit a related binding mode
