FIGURE 4.
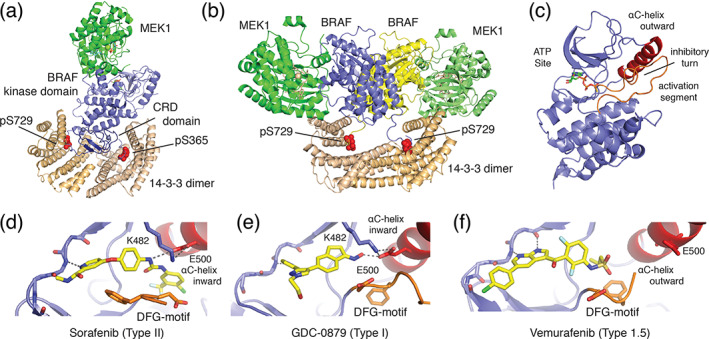
Structural basis for BRAF autoregulation and small‐molecule inhibition. (a) Autoinhibited BRAF:MEK1:14‐3‐3 complex (PDB ID 6NYB) and B) active BRAF:MEK1:14‐3‐3 complex, in which the 14‐3‐3 dimer rearranges to bind the C‐terminal pSer729 site of two BRAF protomers to form the active back‐to‐back BRAF kinase dimer (PDB ID 6Q0J). 77 The Ras‐binding domain is not visualized in these structures. (c) Zoom in on BRAF kinase domain (PDB ID 6NYB) from autoinhibited complex. Key structural features of the autoinhibited state are labeled. 77 (d–f) Binding modes of representative classes of BRAF inhibitor, including (d) Sorafenib (Type II, PDB ID 1UWH), 79 (e) GCD‐0879 (Type I, PDB ID 4MNF), 80 and vemurafenib (Type 1.5, PBD ID 3OG7) 81 showing defining orientations of the DFG‐motif (orange) and αC‐helix (red)
