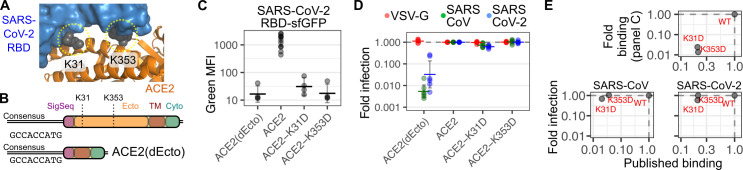
Fig 2. ACE2 variant expressed at high abundance levels.
A) The location of ACE2 (orange) K31 and K353 residues (grey) in the interface with SARS-CoV-2 RBD (blue); with the three-dimensional structure provided by PDB 6M17. B) Schematic showing the coding region of the ACE2 expression construct, as well as the dEcto negative control construct lacking the entire extracellular domain. C) ACE2 variant constructs encoding the consensus Kozak, stained with SARS-CoV-2 RBD-sfGFP. n = 4 or more, error bars denote 95% confidence intervals. D) Pseudovirus infection rates of ACE2 variants encoding the consensus Kozak, normalized to cells encoding WT ACE2. n = 6, error bars denote 95% confidence intervals. E) Scatterplots depicting pseudovirus infection or SARS-CoV-2 RBD-sfGFP staining of cells encoding consensus Kozak ACE2 preceding WT, K31D, or K353D ACE2, compared to published binding studies with SARS-CoV or SARS-CoV-2 RBDs.