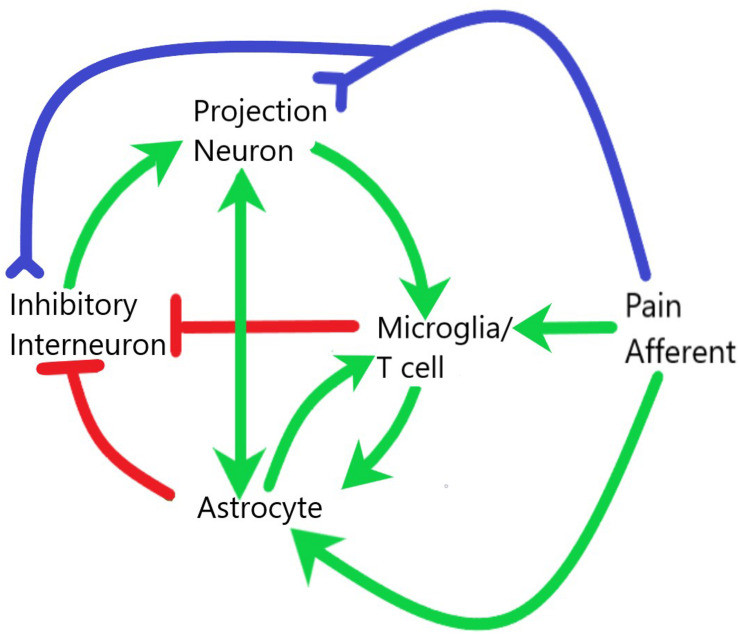
FIGURE 2.
Interaction of glial and neuronal cells within the spinal cord during central sensitization and neuroinflammation. Pain afferents are subject to neuropathic or inflammatory insult and signals of real or potential tissue damage are sent to both the projection neurons and inhibitory interneurons within the dorsal horn of the spinal cord. The release of neuropeptides in the synaptic cleft as well as the increased electrical activity at these synapses leads to activation of both microglia and astrocytes. These glial cells then interact with each other and with neurons to establish a systemic positive feedback system that is self-sustaining. Green lines demarcate activation, red lines demarcate inhibition, blue lines demarcate axonal connection.