Fig. 1.
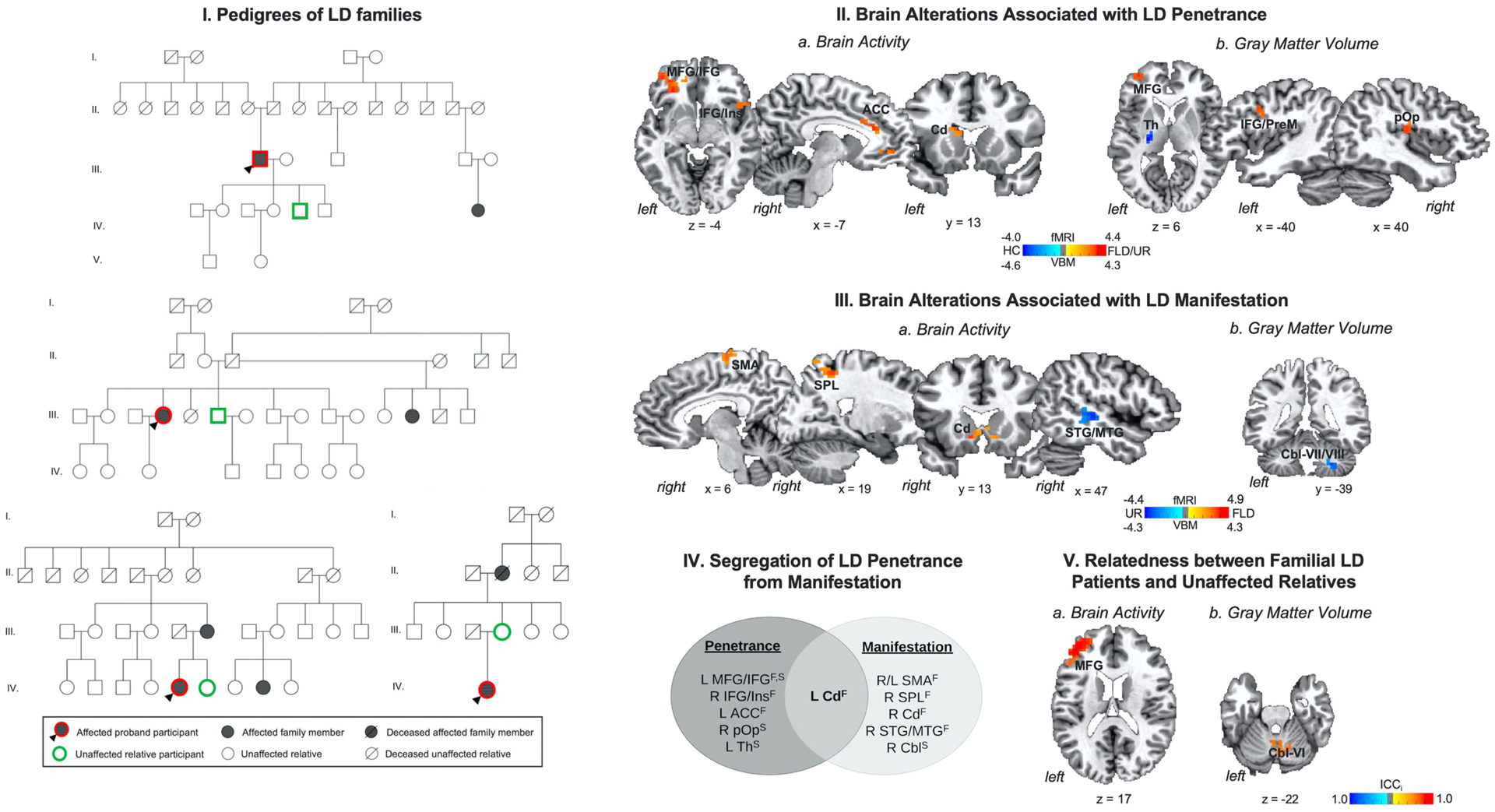
(I) Example pedigrees of families of patients with laryngeal dystonia (LD). (II) Brain alterations associated with LD penetrance are based on differences in (a) brain activity and (b) gray matter volume in familial LD patients and their unaffected relatives vs. healthy controls. (III) Brain alterations associated with LD manifestation are based on differences in (a) brain activity and (b) gray matter volume in familial LD patients vs. their unaffected relatives. (IV) Schematic of functional and structural alterations segregating LD penetrance from manifestation. (V) Relatedness between patients with familial LD and their unaffected relatives as a function of (a) brain activity and (b) gray matter volume. Brain alterations are shown on a series of axial, sagittal or coronal brain slices in the AFNI standard Talairach-Tournoux space. The color bar indicates the z-statistics in (II, III) and the intraclass correlation index (ICCi) in (V). Abbreviations: ACC - anterior cingulate cortex, Cbl - cerebellum, Cd - caudate nucleus, F – functional alteration, FLD – familial laryngeal dystonia patients, HC – healthy controls, ICCi – intraclass correlation index, IFG - inferior frontal gyrus, Ins – insula, L – left, MFG - middle frontal gyrus, MTG - middle temporal gyrus, PrM - premotor cortex, pOp - parietal operculum, R – right, SMA - supplementary motor area, SPL - superior parietal lobule, STG - superior temporal gyrus, S – structural alteration, Th – thalamus, UR – unaffected relatives.
