Fig. 3.
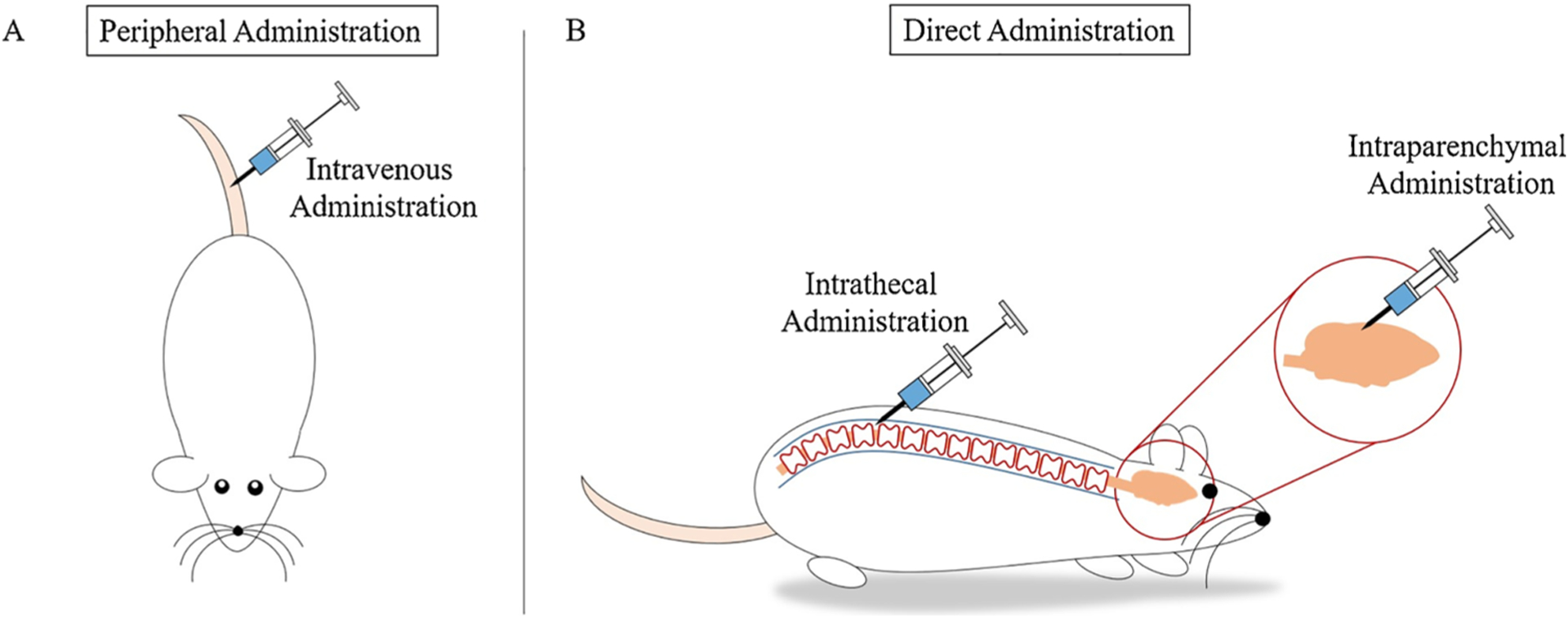
Genes are delivered through various routes of administration. A) Peripheral administration is a common route of administration in vivo and is often achieved by intravenous injection via the tail vein of a rat or mouse. Following peripheral administration, the gene delivery system must cross the BBB to enter the CNS. B) Direct administration allows researchers to bypass the BBB and directly inject the gene delivery system into the CNS. Two common routes of direct administration into the CNS are intrathecal administration and intraparenchymal administration. Following intrathecal administration, via injection into the subarachnoid space, the gene delivery system enters the cerebrospinal fluid and is delivered throughout the CNS. Following intraparenchymal administration, via injection into the brain parenchyma, the gene delivery system enters the brain parenchyma and is delivered locally in the brain.
