Figure 7.
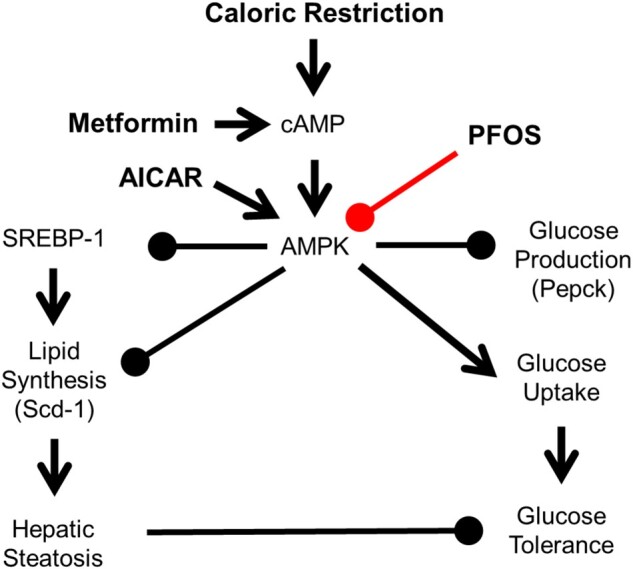
Hypothesis mechanism of PFOS effects in lipid and glucose signaling. AMPK is activated by phosphorylation in response to increases in the cellular AMP:ATP ratio, which is increased by CR or metformin. AMPK can also be directly activated by 5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide-1-beta-D-ribofuranoside (AICAR). Once activated, AMPK inhibits hepatic glucose production and lipid synthesis via SREBP-1. AMPK can induce glucose production via insulin signaling. Inhibiting AMPK activation can lead to hepatic steatosis and glucose intolerance.
