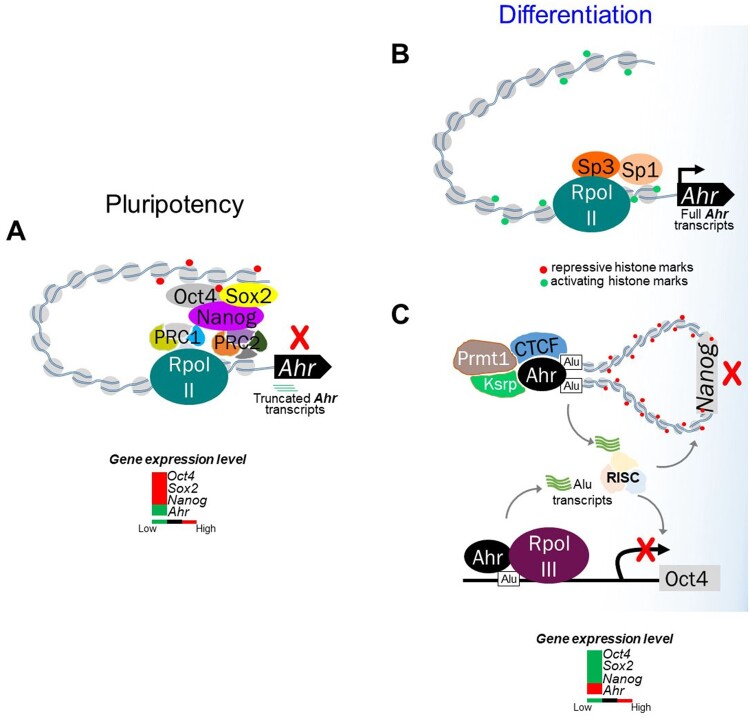
Figure 1.
Crosstalk between the AHR and pluripotency factor in pluripotent state and during differentiation. A, In pluripotent ES cells, complexes of OCT4, NANOG, and SOX2 cooperate with Polycomb Group Repressive Complexes PRC1/2 to bind to a distal silencer domain in the Ahr upstream region and actively repress AHR expression. Unproductive RNA polymerase II is paused at the Ahr transcription start site and drives the synthesis of short abortive transcripts. B, During differentiation, AHR expression is derepressed by reversal of repressive marks in the Ahr promoter chromatin, release of pluripotency factors and PcG proteins, binding of Sp factors, establishment of histone marks of open chromatin, and engagement of active RNAPII to drive full-length RNA transcript elongation. C, In human embryonal carcinoma cells, AHR suppresses OCT4 and NANOG expression by binding to flanking Alu elements. This generates short noncoding RNA transcripts that target the degradation of OCT4 and NANOG mRNA through the RISC complex. At the NANOG locus, AHR cooperatively binds with CTCF, thus initiating chromatin looping and heterochromatinization around the NANOG gene leading to silencing of NANOG expression to allow differentiation to proceed.