Fig. 2. Optogenetic perturbation of MEC or LEC selectively affects learning.
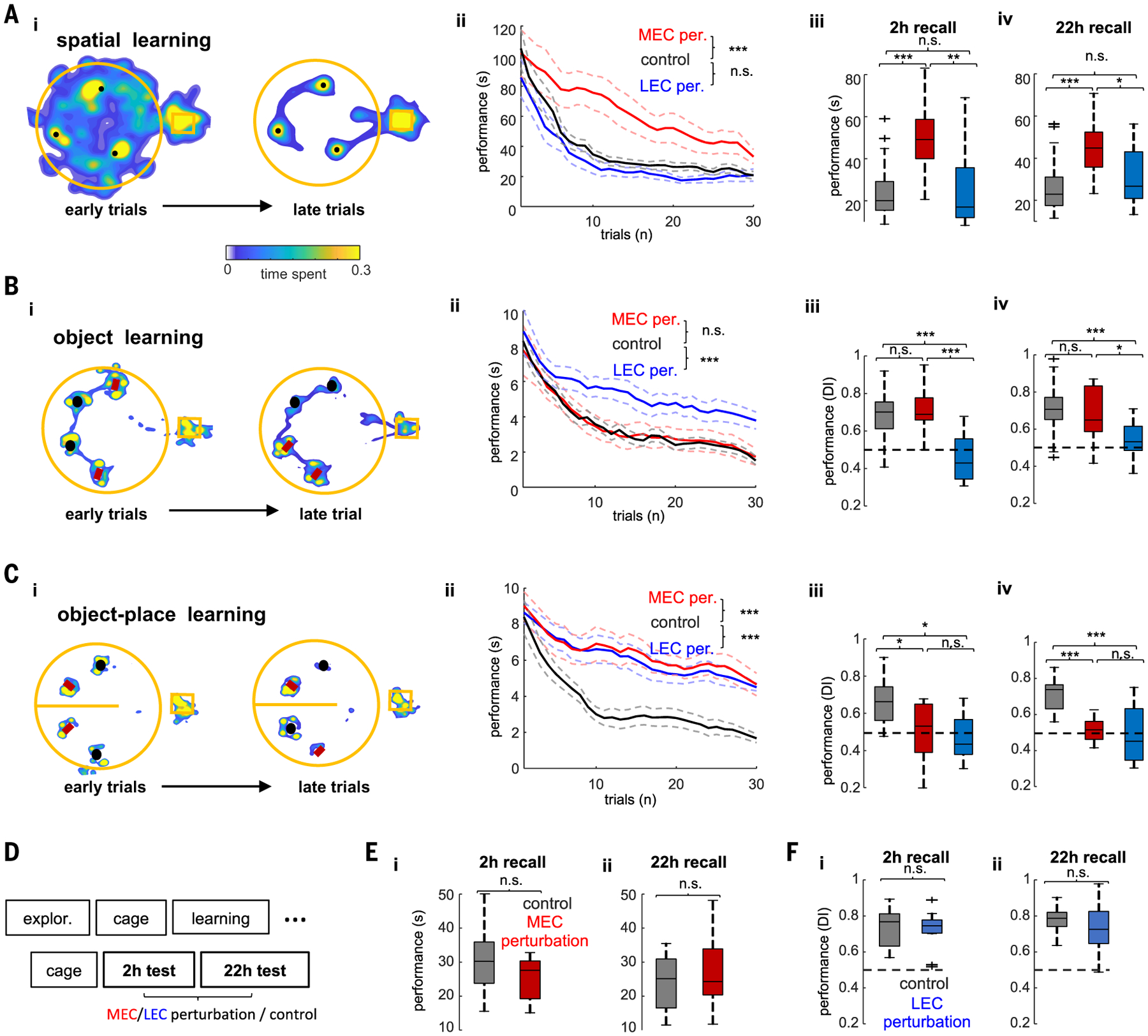
(A) Spatial learning task. (i) Example occupancy maps of the first three (left) and last three (right) learning trials. Black dots indicate locations of hidden water rewards. (ii) Learning performance quantified as time spent to find the three rewards during control (no stimulation) and MEC and LEC perturbation sessions (n = 6/6 rats in MEC and LEC tests, respectively). ANOVA with repeated measures showed a significant main effect of group (F(2,60) = 93.96, P < 10−10). (iii and iv) Memory performance during recall test 2 hours after learning (F(2,60)= 16.7, P = 1.4 × 10−6, one-way ANOVA) (iii) and 22 hours after learning (F(2,60) = 10.62, P = 1 × 10−4, one-way ANOVA) (iv). (B) Same layout as in (A) but in the object learning task. Objects marked with red rectangles cued the location of reward. Black circles indicate distractor objects. (ii) Learning performance was quantified as time spent exploring around distractor objects [same 6/6 rats as in (F); F(2,57) = 51.61, P < 10−10, repeated-measures ANOVA for group effect]. (iii and iv) Memory recall at 2 hours (iii) or 22 hours (iv) after learning was quantified with a DI (see the materials and methods; F(2,57) = 21.55, P = 7.8 × 10−8 and F(2,57) = 9.12, P = 4 × 10−4, for the 2-hour and 22-hour tests, respectively). (C) Object-in-place learning task. Same layout as in (A). In the right side of the maze (top part in the figure), the red object was rewarded and the black one served as a distractor. In the left side (bottom part in the figure), the black object was rewarded and the red one served as a distractor. Learning performance was quantified as in the object learning task (n = 4/4 rats in MEC and LEC tests). ANOVA with repeated measures showed a significant main effect of group during learning trials (F(2,44) = 136.87, P < 10−10). Memory performance was also disrupted 2 hours after learning (F(2,44)= 5.7, P = 7.6 × 10−3) and 22 hours after learning (F(2,44)= 13.39, P = 6.9 × 10−5). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, Tukey’s post hoc test. (E) Timeline of the experiment for testing the effect of MEC and/or LEC perturbation during postlearning test sessions. (F) Memory performance in the spatial memory task for control and MEC perturbation sessions during recall test 2 hours after learning (P = 0.35, rank-sum test) (i) and 22 hours after learning (P = 0.78) (ii). (G) Memory performance in the object memory task for control and LEC perturbation sessions during recall test 2 hours (P = 0.83) (i) and 22 (ii) hours after learning (P = 0.26, rank-sum test).
