Fig. 6. Neuronal assembly composition is task specific.
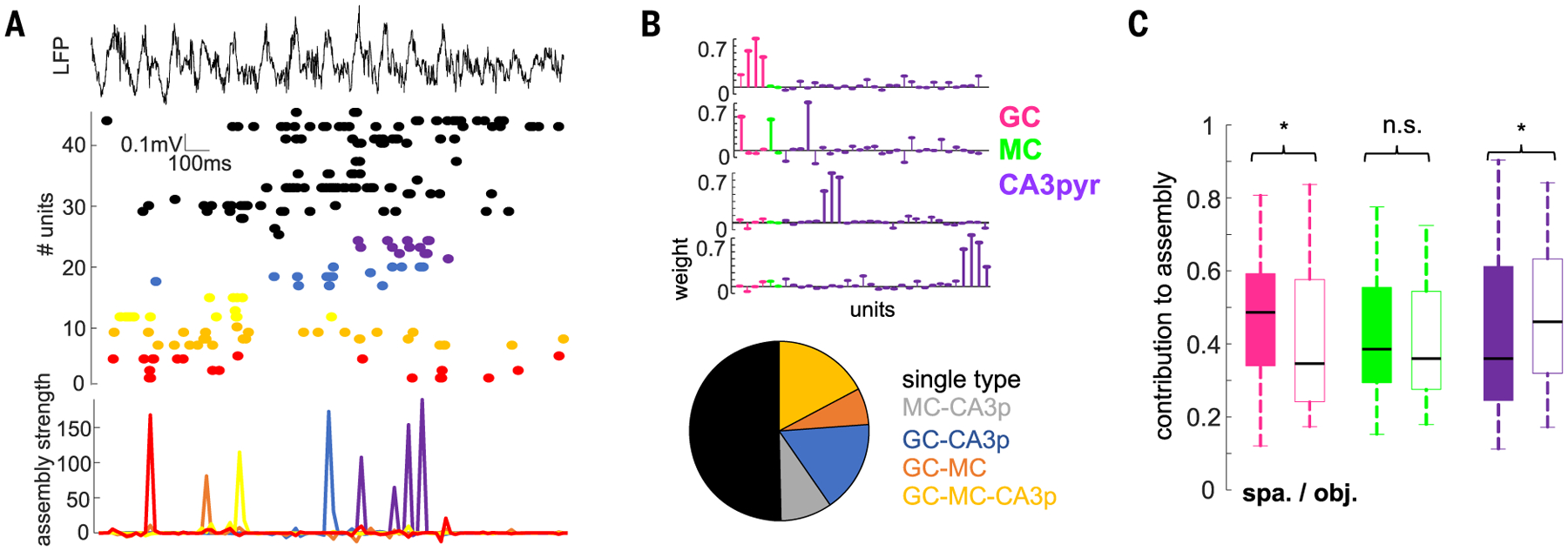
(A) Activation of cell assemblies during an example learning trial. Shown is a LFP and raster plot of spiking of simultaneously recorded neurons (top, middle; color-coded) and activation of individual assemblies (bottom). For this figure, a 20-ms time window was used for assembly detection (see the materials and methods). (B) Weight vectors of three representative assemblies in one session (top) and proportion of assemblies (bottom) with GCs, MCs, or CA3pyr cell members or their combinations (n = 182 assemblies from 20 rats). (C) Cell-type contribution to assemblies in the spatial and object learning tasks (n = 77/83 GCs 36/44 MCs, and 237/186 CA3pyr cell assembly members in spatial and object tasks; F(647,2) = 5.37, P = 4.8 × 10−3, two-way ANOVA). *P < 0.05, rank-sum test.
