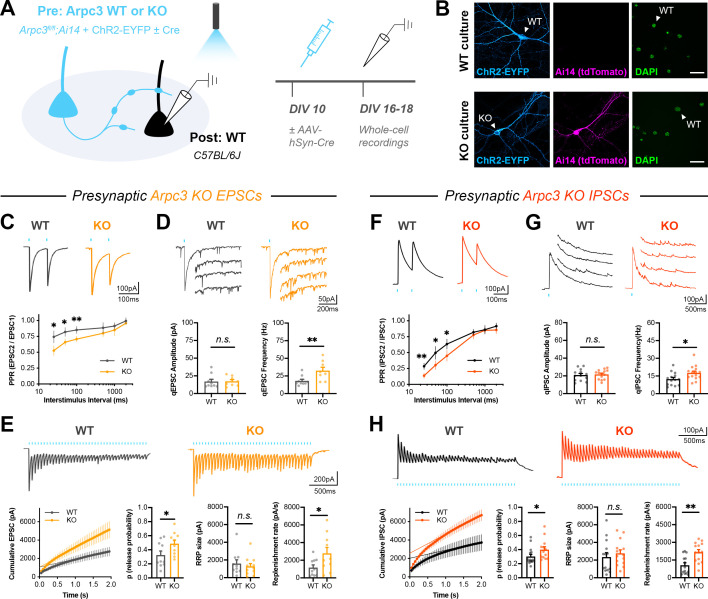
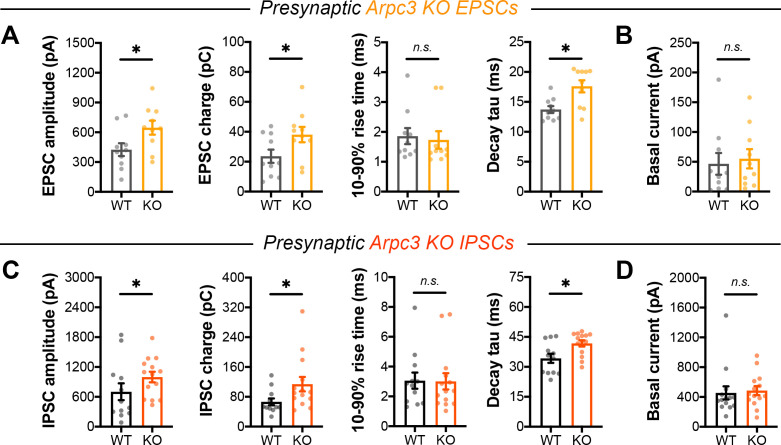
Figure 5. Presynaptic Arp2/3 negatively regulates release probability and synaptic vesicle replenishment.
(A) Schematic of mixed hippocampal neuron cultures to isolate effects of presynaptic Arpc3 knockout. (B) Representative images of WT and KO cultures fixed on DIV16 and stained for ChR2-EYFP (blue), tdTomato (magenta), and DAPI (green). Scale bars, 25 μm. (C–E) Light-evoked EPSCs in WT and KO cultures. Traces and quantification for: (C) PPR (WT n=10 neurons/3 cultures, KO n=12/3); two-way repeated measures ANOVA (F1,20=22.50, p=0.0001) with Sidak’s multiple comparisons test: 25 ms (p=0.0435), 50 ms (p=0.0194), 100 ms (p=0.0099), 500 ms (p=0.2168), 1000 ms (p=0.2319), 2000 ms (p=0.6130). (D) Strontium-evoked qEPSCs (WT n=9/3, KO n=8/3) with amplitude (U=31, p=0.6730) and frequency (t15=2.973, p=0.0095). (E) 20 Hz stimulation trains (WT n=10/3, KO n=10/3) with release probability (t18=2.107, p=0.0494), RRP size (t18=0.3957, p=0.3957), and replenishment rate (t18=2.215, p=0.0399). (F–H) Light-evoked IPSCs in WT and KO cultures. Traces and quantification for: (F) PPR (WT n=14/3, KO n=13/3); two-way repeated measures ANOVA (F1,25=16.41, p=0.0004) with Sidak’s multiple comparisons test: 25 ms (p=0.0022), 50 ms (p=0.0117), 100 ms (p=0.0111), 500 ms (p=0.4100), 1000 ms (p=0.9999), 2000 ms (p=0.3992). (G) Strontium-evoked qIPSCs (WT n=14/3, KO n=15/3) with amplitude (t27=0.3989, p=0.6931) and frequency (t27=2.471, p=0.0201). (H) 20 Hz stimulation trains (WT n=14/3, KO n=14/3) with release probability (U=52, p=0.0350), RRP size (t26=0.6733, p=0.5067) and replenishment rate (t26=3.621, p=0.0012). All data are mean ± SEM. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, n.s. not significant. t values are t-tests, and U values are Mann-Whitney U-tests.