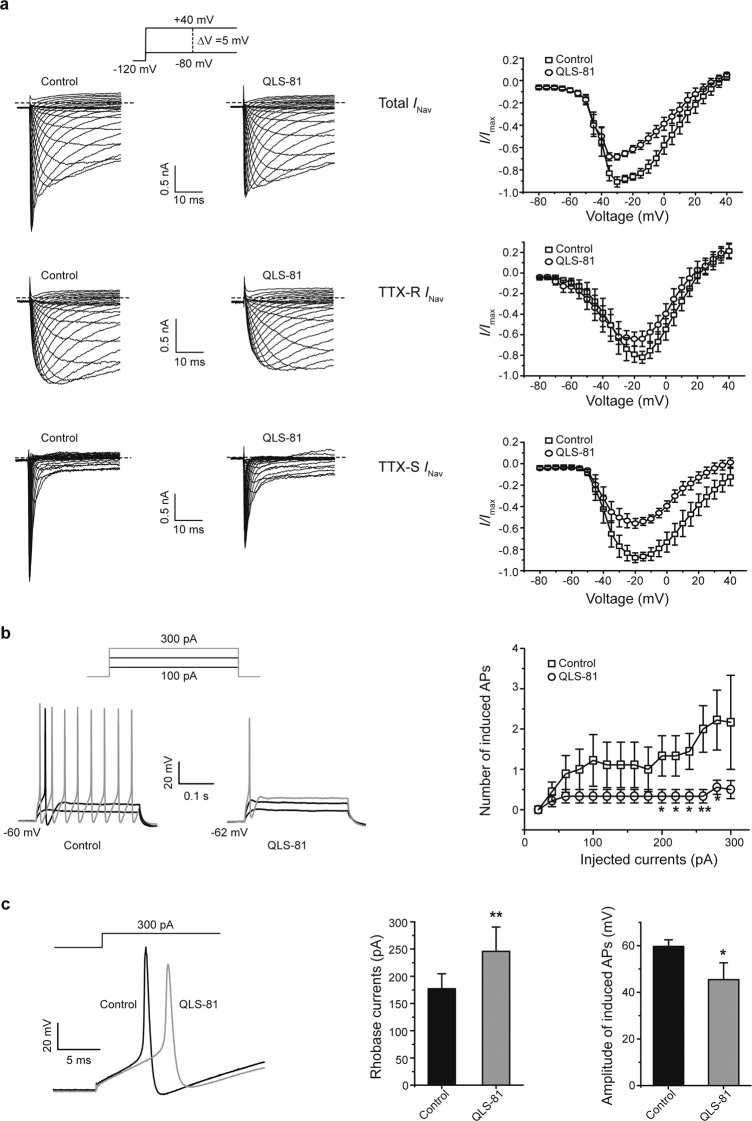
Fig. 4. Inhibition of native Nav currents and firing in DRG neurons by QLS-81.
a Left and middle panels, representative total (top panel) currents, TTX-R (middle panel), and TTX-S (bottom panel) currents in DRG neurons of small or medium size diameter were elicited by a family of depolarizing voltage steps in a 5-mV increment from −80 mV to +40 mV with holding potential at −120 mV in the absence (open squares) or presence (open circles) of 10 μM QLS-81. Right panel, current–voltage (I–V) relationships of peak currents normalized with the maximum amplitude of Nav current obtained from left panels n = 7–8. b Representative traces of action potential (AP) induced by injection of different depolarizing currents without (left panel) or with (middle panel) QLS-81. Right panel, summary for the number of action potentials induced by increasing depolarizing currents with or without QLS-81 (10 μM). Paired t-test, *P < 0.05, and **P < 0.01 vs. Control, n = 9. c Left panel, representative traces of AP induced by injection of 300 pA depolarizing currents with (gray) or without (black) QLS-81 (10 μM). Middle panel, a summary of the depolarization current threshold for eliciting the first AP with or without QLS-81 (10 μM). Right panel, summary for the amplitude of induced APs by injection of 300 pA current with or without QLS-81. Paired t-test, *P < 0.05, and **P < 0.01 vs. Control, n = 9. All data were expressed as the mean ± SEM.