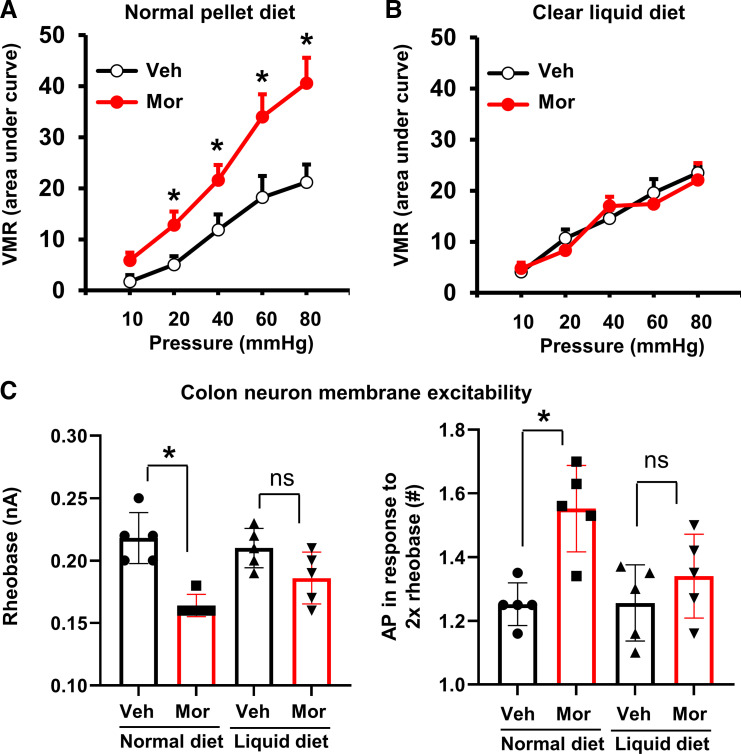
Figure 4.
Opioid-induced visceral hypersensitivity in rats: effect of colon cleansing. The visceromotor response (VMR) was increased significantly by morphine treatment (7 days) in rats when fed a normal pellet food diet (A), but not in rats fed a clear liquid diet (B). Patch-clamp study (C) found that the colon-projecting DRG neurons demonstrated hyperexcitability in Mor rats with decreased rheobase (left) and increased number of action potential in response to 2× rheobase (right), when rats were fed normal pellet food. However, colon cleansing attenuated morphine-induced neuronal hyperexcitability. N = 5 rats in each group, with ∼17–20 neurons recorded for each group in patch-clamp study. *P < 0.05 vs. normal/Veh. P > 0.05. DRG, dorsal root ganglia; Mor, morphine-treated rats; NS, no significant difference; Veh, vehicle control rats.