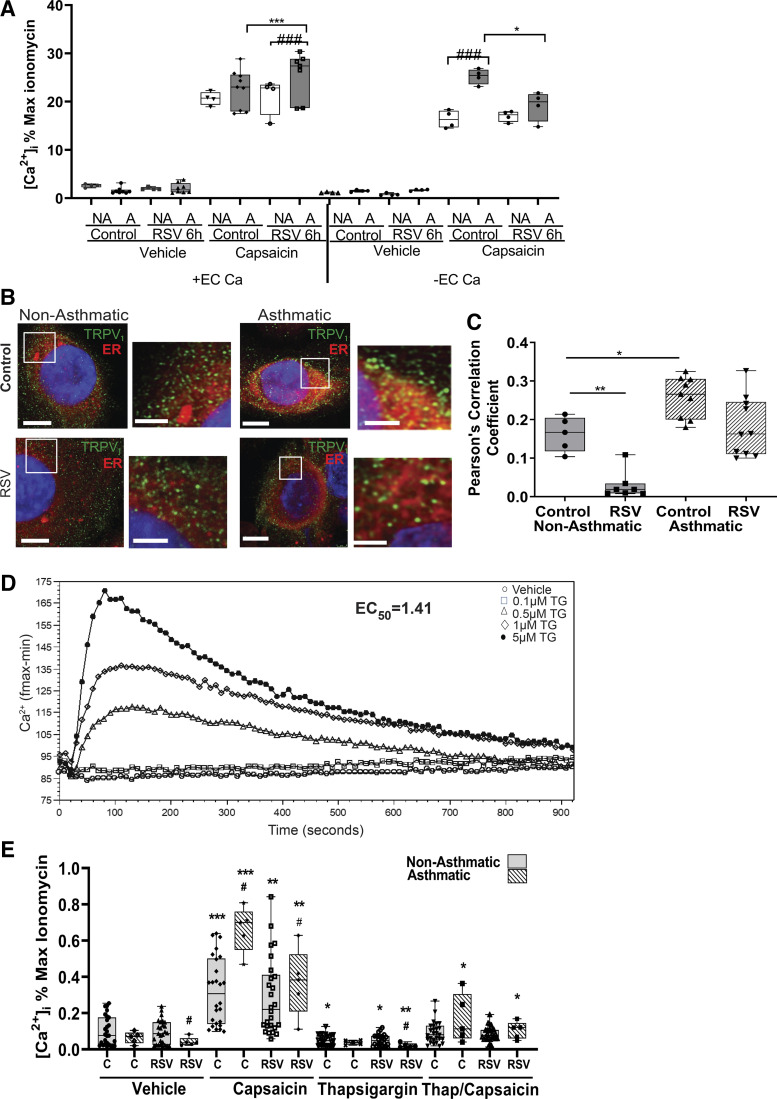
Figure 3.
Role of ER in TRPV1-mediated [Ca2+]i. HBE cells from either children without or with asthma were infected with sterile medium or RSV (MOI = 1) for 6 h before activation of TRPV1 with vehicle (DMSO) or capsaicin (150 µM) in the presence (left) or in the absence (right) of [Ca2+]ec (A). Calcium influx was measured using Calcium 6 dye after TRPV1 activation by vehicle or capsaicin of nonasthmatic (2–4, 7, 10) or asthmatic (12, 13, 15) intact HBE cells. B: representative fluorescent micrographs of colocalization of TRPV1 expression (green) with the ER (Cytopainter ER tracking Dye, red). Images shown are at ×100 magnification and insets are zoomed ×2. Scale bar = 15 µm in ×100 images; scale bar = 5 µm in the zoomed panels. C: Pearson’s correlation coefficient calculated for the colocalization of TRPV1 with ER using Volocity. HBE cells from children without (2–4, 7, 10) and with asthma (12–15) were used in the analysis. D: HBE cells were treated with increasing amounts of TG and calcium levels were measured over 15 min. Calcium influx was measured using Calcium-6 dye after vehicle or TG in intact HBE cells (2, 15). The Softmax-Pro software was used to calculate EC50 = 1.41 µM. Samples were run in triplicate. E: [Ca2+]i in HBE cells stimulated in the absence of [Ca2+]ec. HBE cells from children without (1–4, 7) and with asthma (12, 13, 15) were incubated with sterile medium or RSV (MOI = 1) for 6 h, then pretreated with vehicle or thapsigargin (TG, 1.5 µM) for 30 min before activation of TRPV1 with capsaicin (150 µM). Data are expressed as means ± SE and were analyzed using the Kruskal–Wallis test with Dunn’s multiple comparisons. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 compared with noninfected controls; #P < 0.05, ###P < 0.001 compared with nonasthmatic controls. All experiments were repeated ≥2 times in triplicate. [Ca2+]i, intracellular calcium; ER, endoplasmic reticulum; HBE, human bronchial epithelium; MOI, multiplicity of infection; RSV, respiratory syncytial virus; TRPV1, transient receptor potential vanilloid 1.