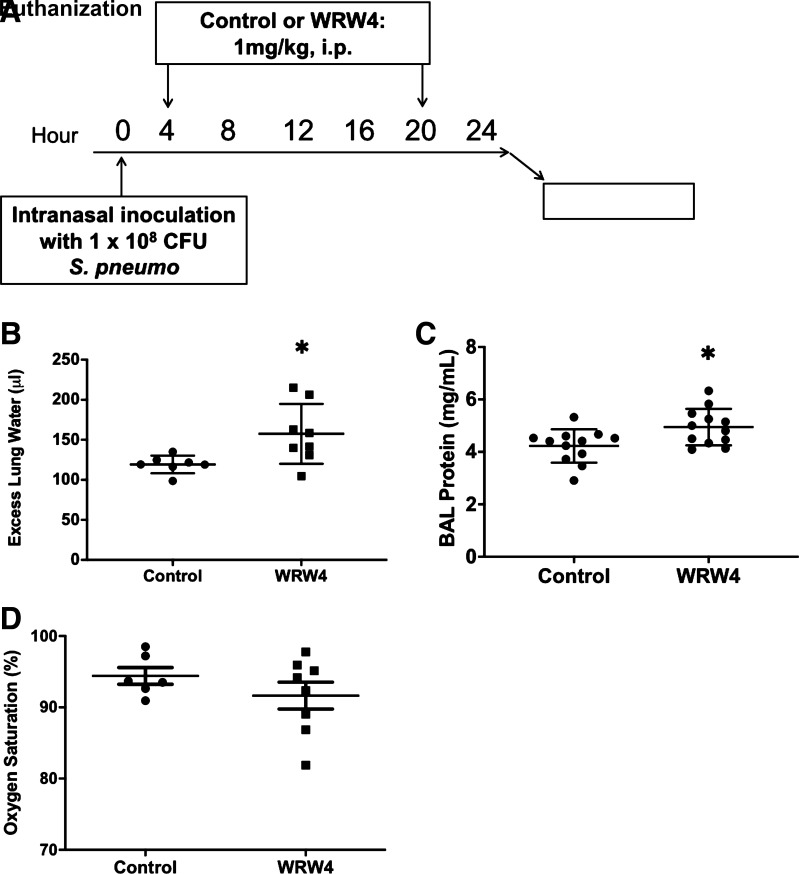
Figure 1.
Pulmonary impact of formyl peptide receptor 2 (ALX/FPR2) inhibition. A: schematic depicting experimental procedures. Mice were inoculated with 1 × 108 CFU of Streptococcus pneumoniae intranasally. Four and 20 hours after induction of injury, mice were either given 1 mg/kg of WRW4 or control (PBS) intraperitoneally (i.p.). Mice were euthanized at 24 h postinfection for bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL). B: pulmonary edema, as measured by excess lung water (ELW) in the interstitial and alveolar spaces, was increased in the mice that received WRW4 (n = 8) compared with those that received control (n = 7). *P = 0.02. C: BAL protein was increased in the mice that received WRW4 (n = 12) compared with those that received control (n = 12). *P = 0.02. D: mean arterial oxygenation saturation in mice given either WRW4 (n = 8) or control (n = 6). P = 0.27. CFU, colony-forming units.