Figure 1.
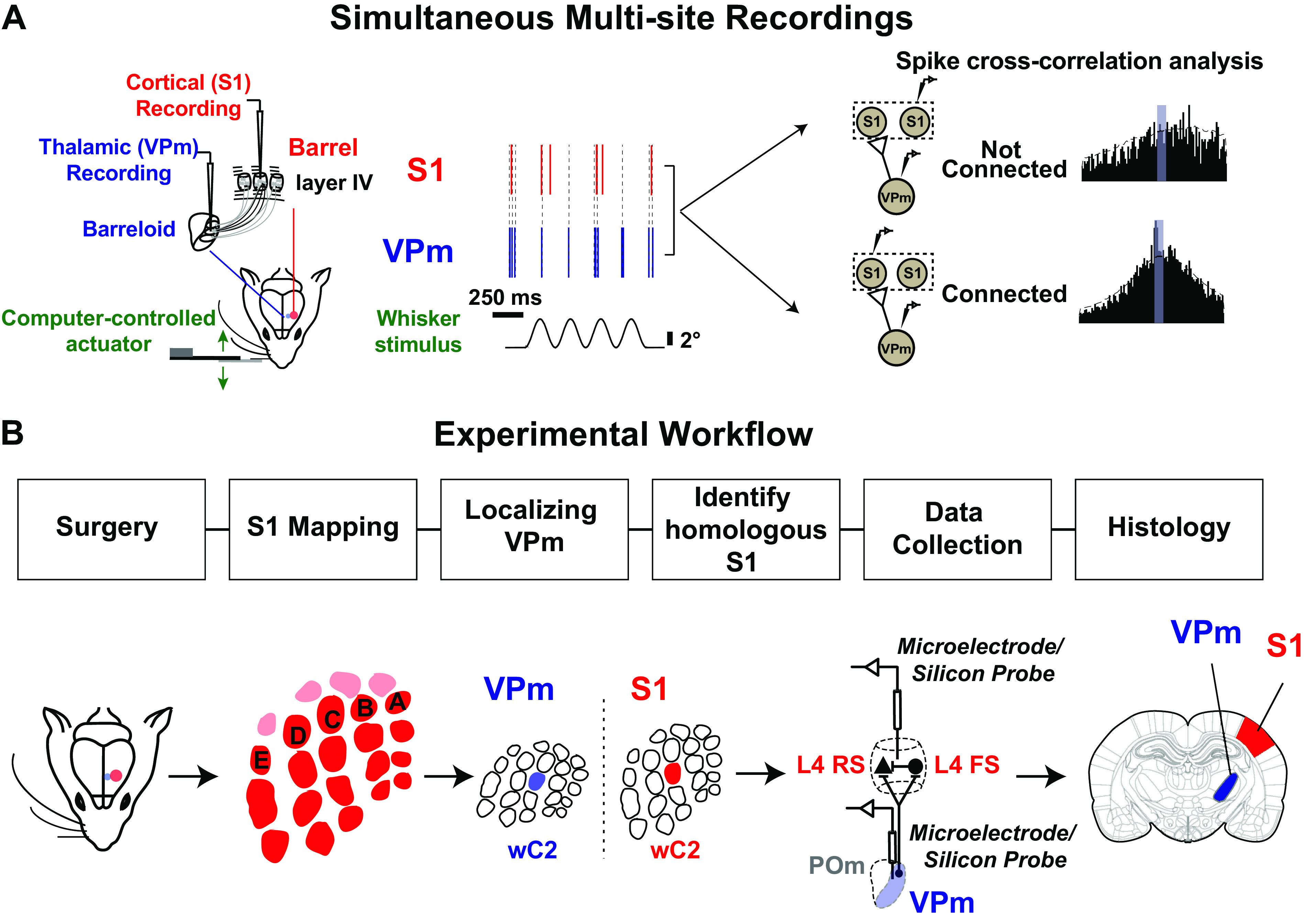
Experimental approach used to estimate monosynaptic connectivity between somatotopically organized areas of the rodent somatosensory pathway. A: simultaneous single-unit extracellular recordings were performed in the ventral posteromedial nucleus (VPm) of the thalamus and in layer IV of primary somatosensory cortex (S1) in anesthetized rodents. Recordings were targeted to topographically aligned barreloids in VPm and barrel column in S1. Weak stimulation was applied to the whisker corresponding to the recorded barreloid/barrel column to elicit nonsynchronous spiking. Putative monosynaptic connections between pairs of neurons were inferred with cross correlation analysis. B: experimental procedures used to establish paired recordings involve 1) animal preparation including surgeries; 2) S1 mapping; 3) identification of the whisker corresponding to the recorded barreloid; 4) targeting corresponding S1 barrel column and layer IV; 5) data collection for assessing monosynaptic connectivity by generating spikes via whisker stimulation; repeating steps 3, 4, and 5 for recording additional pairs; and 6) histology. FS, fast-spiking unit; L4, layer 4; POm, posteromedial nucleus; RS, regular-spiking unit; wC2, C2 whisker.
