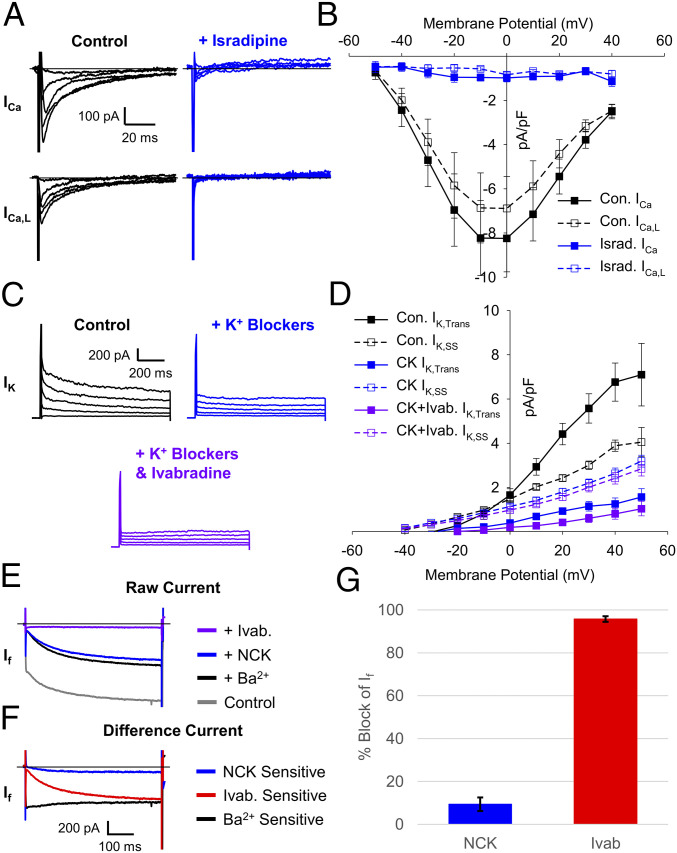
Fig. 2.
The NCK cocktail blocks ivabradine off target effects but not If. (A) Representative total (Top) and L-type (Bottom) whole-cell Ca2+ currents recorded from SAMs in control (black) and after perfusion of 3 µM isradipine (blue). (B) Mean (± SEM) total (closed) and L-type (open) Ca2+-current density in control and after perfusion of 3 µM isradipine using the same color scheme as B. (C) Representative K+ currents in a SAM recorded in control conditions (black) after perfusion of a K+ channel–blocker cocktail (1 mM BaCl2, 10 mM TEA, and 3 μM E-4031; blue) and after subsequent perfusion of the K+ channel–blocker cocktail plus 30 µM ivabradine (purple). (D) Average (± SEM) transient (closed) and steady-state (open) K+-current density in control conditions after perfusion of a K+ channel–blocker cocktail and after subsequent perfusion of 30 µM ivabradine and a K+ channel–blocker cocktail using the same color scheme as C. (E) Representative currents recorded from a murine SAM in response to hyperpolarizing voltage steps to −130 mV from a holding potential of −60 mV in Tyrode’s solution (gray), in Tyrode’s after application of 1 mM barium (black), the NCK-blocker cocktail (blue), or the NCK cocktail with 30 µM ivabradine (purple). (F) Representative difference currents sensitive to 1 mM barium compared to control (black), NCK cocktail compared to barium alone (blue), and the NCK cocktail with 30 µM ivabradine compared to the NCK cocktail alone (red). (G) Average (± SEM) fraction of If blocked by the NCK cocktail (blue) or the NCK cocktail with 30 µM ivabradine (red) during pulses to −130 mV in murine SAMs. Horizontal lines indicate zero current. Number of replicates and details of statistical tests can be found in SI Appendix, Table S2.