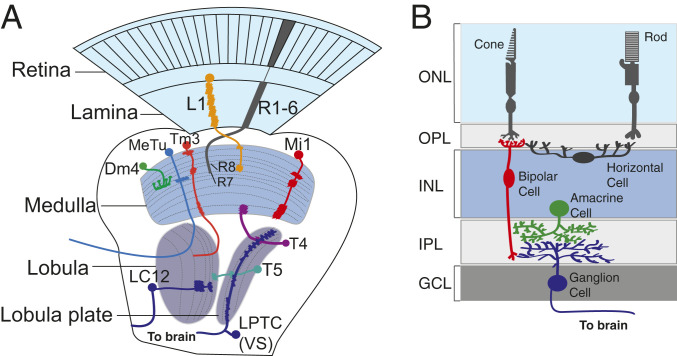
Fig. 1.
Drosophila and mammalian visual system organization. (A) Visual input in Drosophila is captured by photoreceptors divided into ∼800 ommatidia. Outer photoreceptor axons (R1 to R6) project to the cartridges of the lamina, while inner photoreceptor axons (R7 to R8) project to the medulla. Lamina neurons (e.g., L1) also project their axons to the medulla (orange–yellow). Medulla neurons can be divided into numerous classes. Mi neurons (Mi1; red) project their arbors throughout the entire medulla. Transmedullary neurons (e.g., Tm3; orange) connect the medulla to the lobula. Distal medulla (e.g., Dm4; green) neurons are multicolumnar and project arbors across multiple medulla columns. The lobula and lobula plate neuropils are responsible for processing different aspects of vision. T4 neurons (purple) connect the lobula plate to the proximal medulla, while T5 neurons (teal) connect the lobula/lobula plate, which processes broad field motion. LC (e.g., LC12) neurons (dark blue) project within the lobula and send an arbor to the central brain to process various visual features. LPTCs (e.g., VS neurons) are sensitive to wide-field motion and project their arbors to the central brain, as do medulla tubercule (bright blue) neurons. (B) Input to the mammalian visual system is captured by photoreceptors, which are categorized as dim light–sensing rods or bright light/color–sensing cones. Rod and cone photoreceptors synapse onto rod or cone bipolar cells (red), respectively. Horizontal cells (dark gray) integrate the input from multiple photoreceptor cells to bipolar cells. Bipolar cells (red) make synapses with feature-detecting RGCs (blue). RGCs project neurites to higher-order processing centers. Amacrine cells (green) modulate bipolar to RGC signaling. Like Dm neurons in the fly, they are broadly arborizing. Müller glia are integral to visual system processing but are not shown in the figure. GCL, ganglion cell layer; INL, inner nuclear layer; IPL, inner plexiform layer; ONL, outer nuclear layer; OPL, outer plexiform layer.