FIGURE 3.
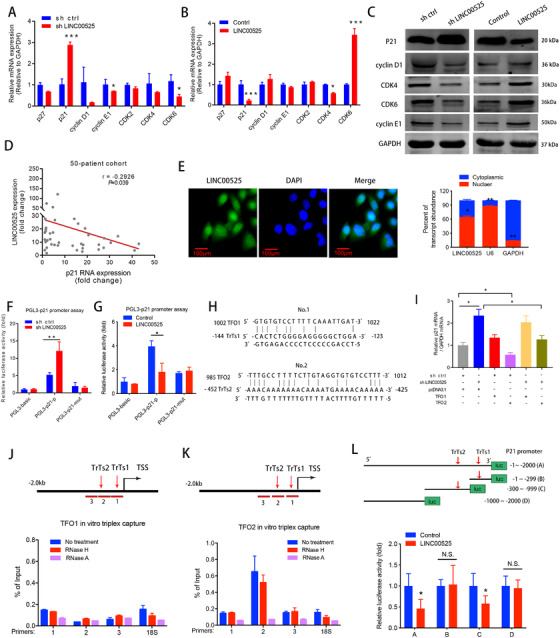
LINC00525 forms a triplex with the p21 promoter to inhibits p21 gene transcription. A‐B. qRT‐PCR analysis of the expression of G1 to S phase transition‐related genes in A549 cells following knockdown (A), or overexpression (B) of LINC00525. C. Western blotting demonstrated that knockdown of LINC00525 increased the expression of P21 protein and decreased the expressions of cyclin D1, cyclin E1, CDK4 and CDK6, whereas overexpression of LINC00525 had an opposite result. D. The expression of LINC00525 was negatively correlated with p21 mRNA as determined by qRT‐PCR in a 50‐patient cohort from Jiangsu Cancer Hospital. E, Florescence in situ hybridization (FISH), and the nuclear mass separation assays suggest that LINC00525 is distributed both in the nucleus and cytoplasm. F‐G. Dual‐luciferase reporter assays showed that LINC00525 inhibited the transcriptional activity of the p21 promoter. H. The potential binding sites of triplex‐forming oligonucleotides (TFOs) within LINC00525 and triplex target site (TrTs) in the promoter of p21 were predicted using the LongTarget program. I qRT‐PCR analysis indicated that overexpression of TFO2, but not TFO1, rescued the increase in p21 expression caused by LINC00525 knockdown. J‐K. Triplex‐capture assay was used to examine the binding of biotin‐labeled TFO1 (J) and TFO2 (K) and three diverse p21 promoter fragments in A549 cells. Triplex‐qPCR suggested that TFO2 formed a triplex structure (presented as a percentage of input) within the p21 promoter. Chromatin was pretreated with RNase A or RNase H. L. Luciferase activities of wildtype and truncated p21 promoter luciferase activities were evaluated by luciferase promoter assay in LINC00525‐overexpressing A549 cells. *, P <0.05; **P <0.01; ***P < 0.001. Error bars, SEM. Abbreviations: N.S, not significant. TFOs, triplex‐forming oligonucleotides; TrTs, triplex target sites; TSS: transcription start site; FISH, florescence in situ hybridization; qRT‐PCR, quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction
