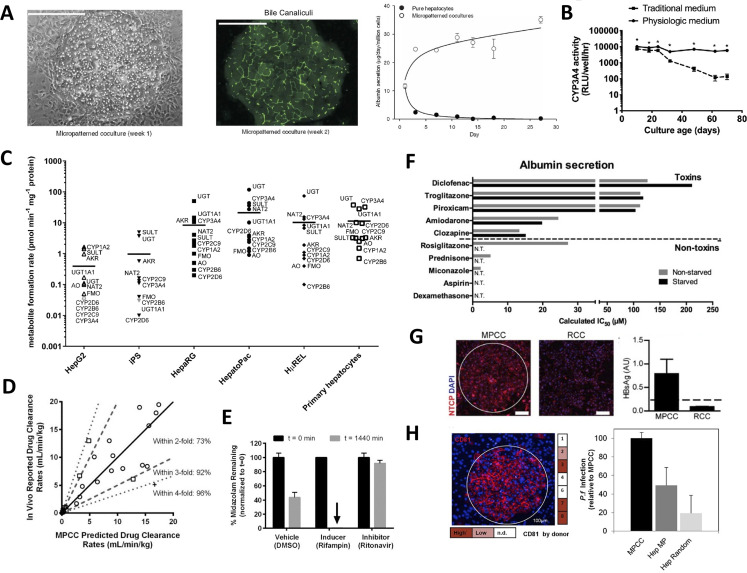
FIG. 2.
Micropatterned cocultures (MPCCs). (a) Primary human hepatocytes (PHH) display prototypical morphology (left, phase contrast), bile canaliculi formation (middle, transport of fluorescent dye), and relatively stable albumin secretion (right) within micropatterned clusters of empirically optimized dimensions and when surrounded by 3T3-J2 murine embryonic fibroblasts.7 Reproduced with permission from Khetani and Bhatia, Nat. Biotechnol. 26(1), 120 (2008). Copyright 2008 Springer Nature. (b) MPCCs subjected to a physiologically inspired medium containing human serum and physiologic insulin levels improved stability of functions (CYP3A4 shown here) to almost 10 weeks as compared to the use of the traditional (bovine serum, high insulin) culture medium utilized in the field of hepatocyte culture systems for drug screening.34 Reprinted with permission from Davidson et al., Toxicology 449, 152662 (2021). Copyright 2021 Elsevier. (c) Formation of drug metabolites mediated by different CYP enzymes across different culture models, such as HepG2 and HepaRG cancerous cell lines, induced pluripotent stem (iPSC) cell-derived hepatocyte-like monocultures, PHHs in suspension, randomly distributed cocultures of PHHs and 3T3-J2 fibroblasts (HμREL), and MPCCs (commercial name HepatoPac™). MPCCs had the highest levels of enzymatic activities overall.51 Reprinted with permission from Kratochwil et al., AAPS J. 19(2), 534–550 (2017). Copyright 2017 Author(s), licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. (d) Correlation of clearance rates for 26 compounds (high, medium, and low turnover compounds) obtained from MPCCs and as observed in the clinic.39 Reproduced with permission from Lin et al., Drug Metab. Dispos. 44(1), 127–136 (2016). Copyright 2016 ASPET. (e) Clearance of midazolam, a CYP3A4 substrate, was significantly enhanced when MPCCs were preincubated with CYP3A4 inducer drug, rifampin, and significantly inhibited when MPCCs were preincubated with CYP3A4 inhibitor drug, ritonavir, which is also observed in the clinic in humans.39 Reproduced with permission from Lin et al., Drug Metab. Dispos. 44(1), 127–136 (2016). Copyright 2016 ASPET. (f) Intermittently starving MPCCs of hormones and serum (bovine) every week for 2 days improves functional lifetime and prediction of drug toxicity outcomes as observed with interpolated IC50 values for toxins but lack of such values for non-toxins (N.T. = not toxic); on the other hand, non-starved cultures displayed several false positive compounds.33 Davidson and Khetani, Toxicol. Sci. 174(2), 266–277 (2020). Copyright 2020 Oxford University Press. (g) MPCCs display higher levels of sodium taurocholate co-transporting polypeptide (NTCP) as compared to random distributed cocultures (RCCs), which led to higher infectivity with hepatitis B virus (HBV) as evident from increased levels of shed HBV “s” antigen in supernatants (HBsAg).46 Reproduced with permission from Shlomai et al., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 111(33), 12193–12198 (2014). Copyright 2014 Author(s). (h) CD81, a Plasmodium entry factor, levels were high for 3 PHH donors cultured in MPCCs (left), which led to higher infection of MPCCs with P. falciparum (i.e., malaria) as compared to micropatterned hepatocytes only (Hep MP) or RCCs.47 Reprinted with permission from March et al., Cell Host Microbe 14(1), 104–115 (2013). Copyright 2013 Elsevier.