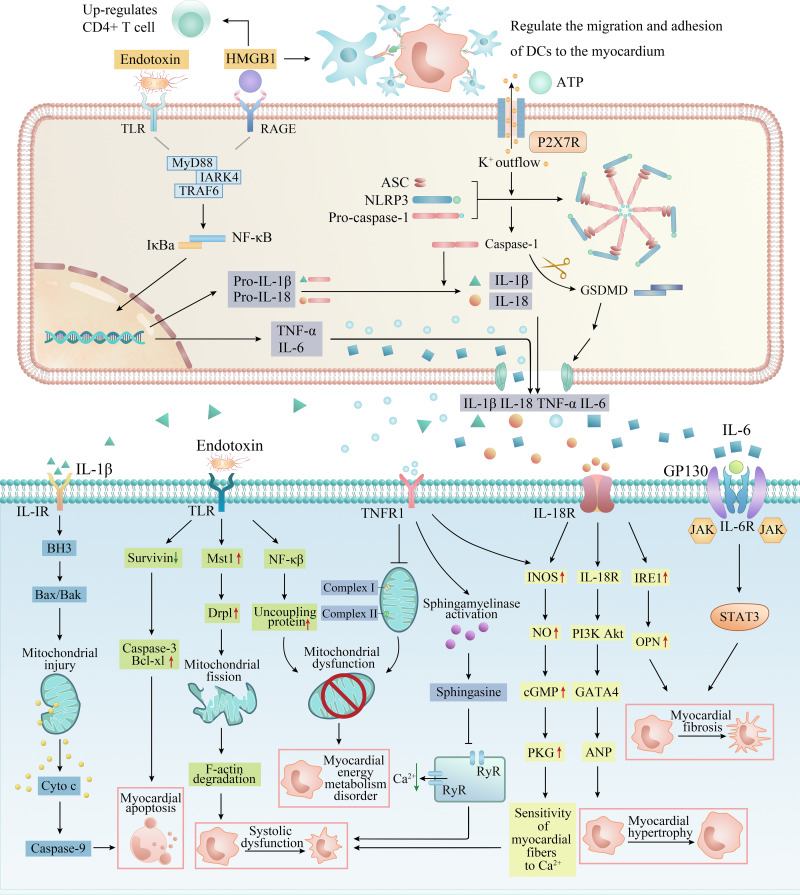
Figure 3.
The specific pathways of myocardial injury and cardiac dysfunction caused by inflammation-related factors. DAMPs and PAMPs such as HMGB1, ATP and endotoxin from the pancreas and intestine act on membrane receptors such as TLR and P2X7R to recruit inflammatory cells (macrophages, neutrophils and dendritic cells) in serum, activate classical inflammatory pathways such as NF-κB and NLRP3 inflammasome in inflammatory cells, release a large number of pro-inflammatory cytokines, and form a cascade reaction (upper). These inflammatory factors eventually act on cardiomyocytes, causing myocardial energy metabolism disorder, systolic myocardial dysfunction, myocardial hypertrophy, apoptosis and fibrosis through a complex network of signaling pathways (lower).