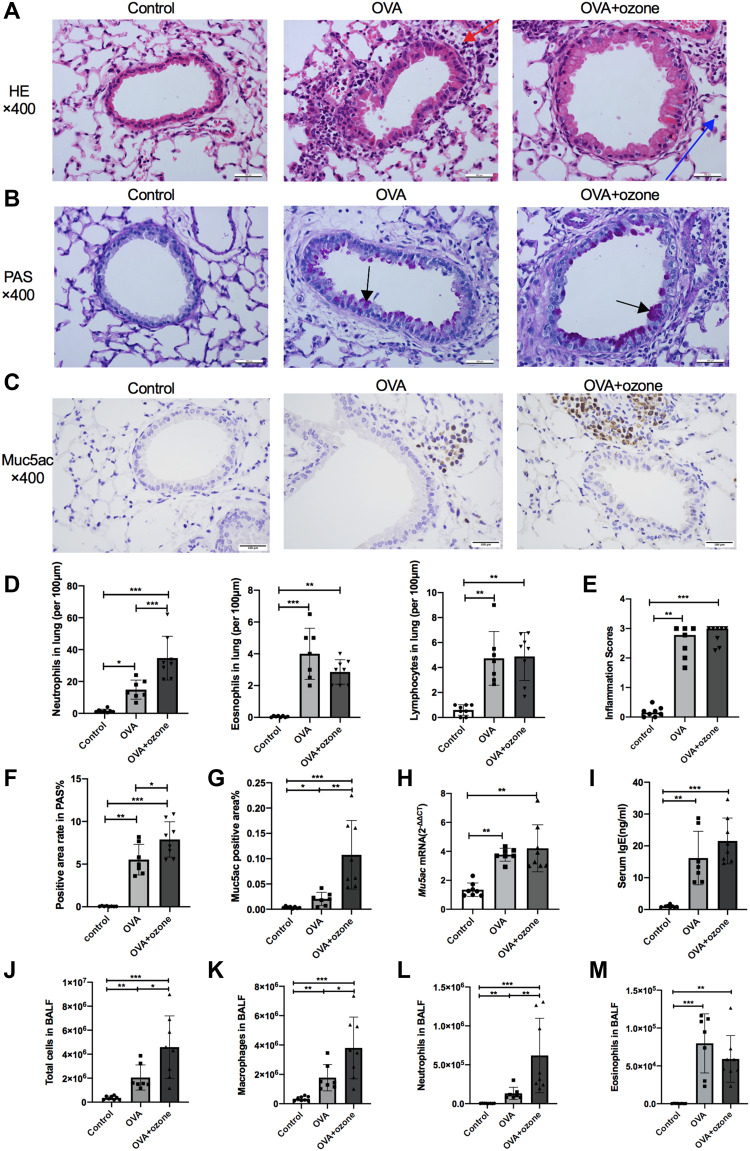
Figure 3.
OVA and OVA + ozone–induced asthma models presented prominent airway inflammation and mucus hypersecretion. The infiltration of neutrophils, eosinophils, and lymphocytes, the PAS-positive area and Muc5ac-positive area were determined in a double-blind design by two investigators independently. Muc5ac mRNA in the lungs of mice was measured by RT-qPCR. (A) Representative photomicrographs of hematoxylin and eosin-stained sections of the lung with inflammatory cell infiltration (a typical neutrophil was indicated by a blue arrow and a typical eosinophil was indicated by a red arrow). (B) Representative photomicrographs of the lung with airway mucus production and goblet cell hyperplasia (purple area within tracheal cavity indicated by arrows). (C) Representative photomicrographs of immunohistochemical analysis of Muc5ac in lung tissue slices. (D) Infiltration density of neutrophils, eosinophils and lymphocytes. (E) Airway inflammation scores. (F) PAS-positive area. (G) Percentage of Muc5ac-positive area around the airways. (H) Muc5ac gene expression in lung tissue. (I) Levels of IgE in serum. (J) Total cells in BALF. (K) Macrophages in BALF. (L) Neutrophils in BALF. (M) Eosinophils in BALF. Scale bars represent 100 µm. Data in (E) are expressed as the median, as they did not fit a Gaussian distribution; other data are expressed as the mean ± SD. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. Scale bars represent 100 µm.
Abbreviation: OVA, ovalbumin.