Figure 3. Cellular roles of ER-phagy and the contributions of metazoan ER-phagy receptors.
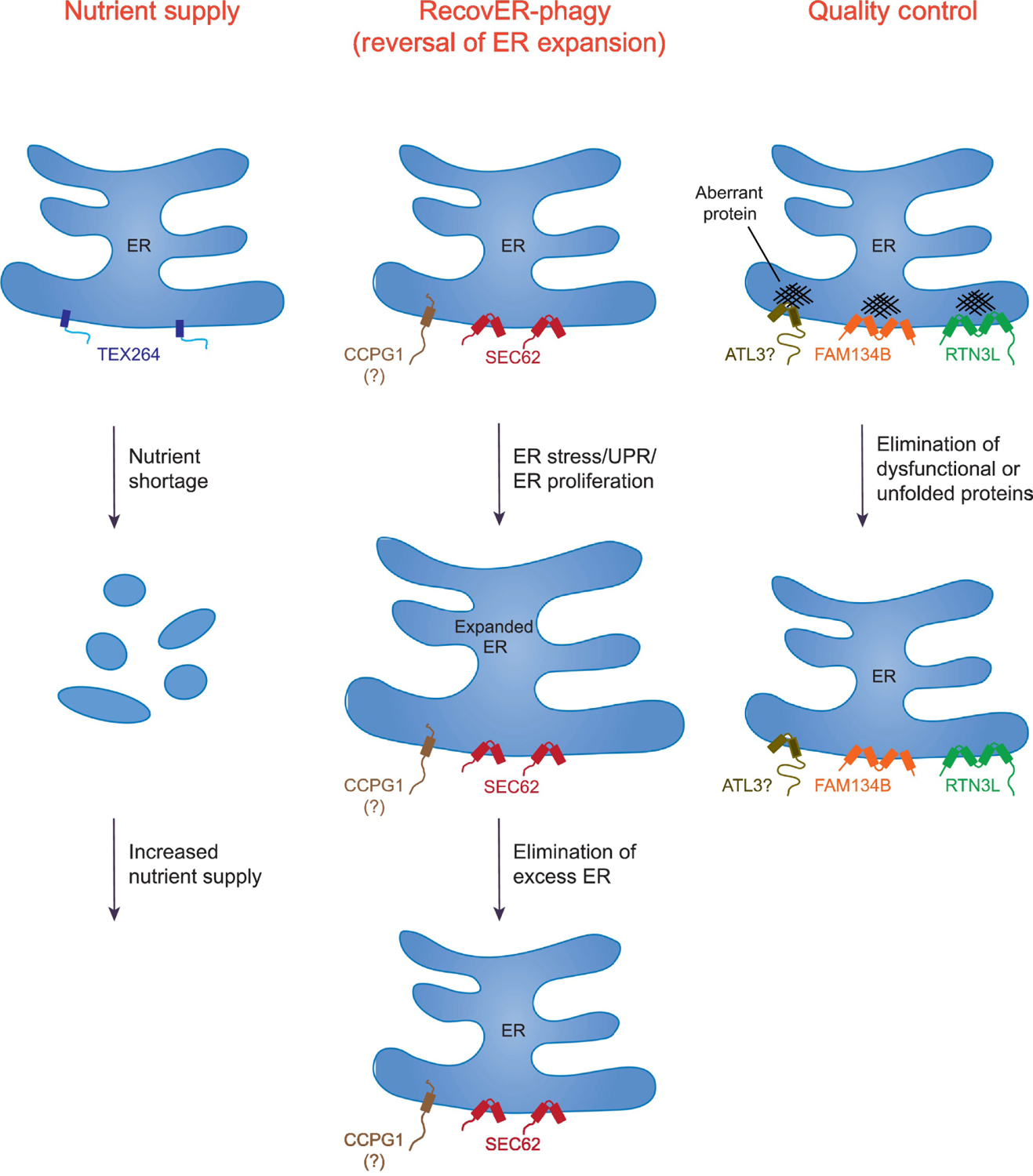
Shown are the general pathways in which ER-phagy is utilized and the contributing receptors. These pathways include: Nutrient Supply (TEX264), RecovER-phagy (Reversal of ER Expansion) (SEC62 and possibly CCPG1), and Quality Control (FAM134B, RTN3L, and possibly ATL3). Not all the listed pathways are limited to the indicated ER-phagy receptors. For example, while TEX264 contributes to ~50% of autophagic flux during amino acid deprivation, other ER receptors, such as FAM134B, can also participate in starvation-induced ER-phagy, albeit far less efficiently. Note that a significant fraction of the ER is fragmented in the Nutrient Supply pathway to illustrate that TEX264 promotes degradation of a large portion of this organelle during amino acid starvation. SEC62 mediates RecovER-phagy. Although CCPG1 function appears to be regulated by the unfolded protein response (UPR), it remains to be determined whether it also definitively participates in RecovER-phagy. In Quality Control, FAM134B facilitates the removal and degradation of misfolded procollagen (shown) and disease-causing mutant NPC1, whereas misfolded pro-insulin (Akita), proopiomelanocortin (POMC) and arginine vasopressin (pro)-AVP utilize RTN3L. There are no known misfolded proteins that specifically utilize ATL3. Also note that FAM134B and RTN3L are inserted into the lipid bilayer via reticulon domains, whereas the other receptors shown possess bona fide transmembrane segments.
