Figure 3. ERG preferentially activates the non-risk allele of NEDD9-Int1Enh.
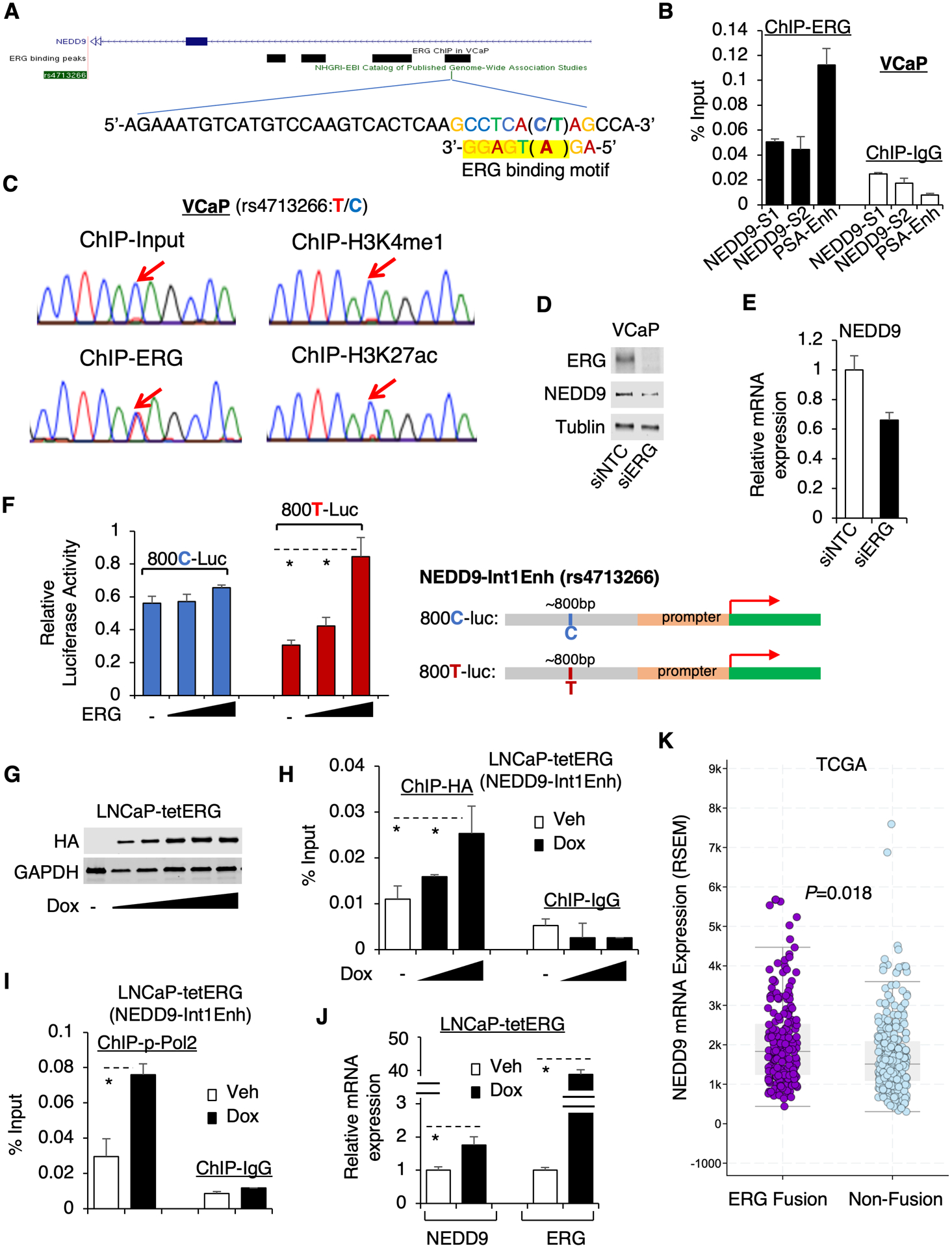
(A) ERG ChIP-seq in VCaP cells indicates ERG binding at NEDD9-Int1-Enh and a putative ERG binding motif at the SNP region was identified (matching sequence highlighted by yellow). (B) ChIP-qPCR for ERG binding at NEDD9-Int1Enh using two primer sets (NEDD9-S1 and S2) in VCaP cells. (C) The extracted DNA from ChIP-ERG, ChIP-H3K4me1, or ChIP-H3K27ac were PCR amplified and then sequenced. (D) Immunoblotting for ERG and NEDD9 in VCaP cells transfected with siRNA against ERG (siERG) or non-target control (siNTC). (E) qRT-PCR for NEDD9 mRNA expression in these cells. (F) DNA fragments (~800bp) containing C or T of rs4713266 were cloned into a luciferase reporter system containing a minimum promoter (800C-Luc and 800T-Luc). PC-3 cells were then transfected with ERG and 800C- or 800T-Luc and the luciferase activities were examined. (G) Immunoblotting for HA in LNCaP cells stably overexpressing doxycycline-inducible HA-tagged ERG (N-terminal 1–44aa truncated) (dox: 0, 0.05, 0.1, 0.2, 0.5, 1μM). (H, I) ChIP-qPCR for HA (dox: 0, 0.1, 0.5 μM) (H) or Ser5-phosphorylated RNA polymerase II (dox: 0, 0.1μM) (I) at NEDD9-Int1Enh site. (J) qRT-PCR for NEDD9 and ERG in this stable cell line treated with doxycycline for 48h. (K) NEDD9 expression in ERG fusion-positive versus fusion-negative PCa by examining the TCGA cohort (data acquired from cBioPortal).
