Figure 4. Molecular chaperones mediate refolding of stockpiled ts p53 at permissive temperature.
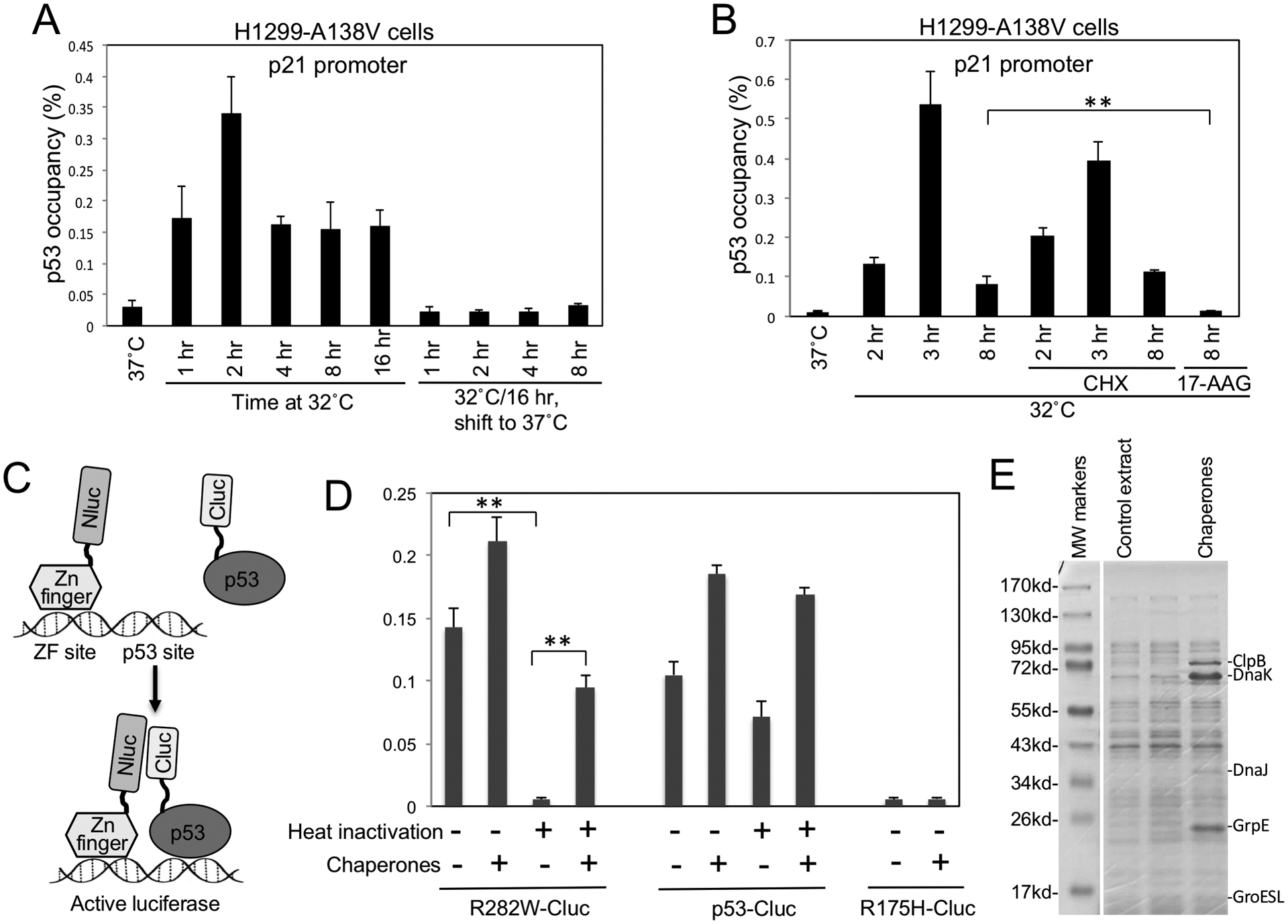
(A) H1299 expressing A138V was shifted from 37°C to 32°C for indicated durations, or pre-incubated at 32°C for 16 hrs and shifted back to 37°C for indicated durations. P53 binding to p21 promoter was determined by ChIP. (B) H1299 cells expressing A138V was shifted to 32°C in the absence or presence of 100 μg/ml cycloheximide (CHX) or 50 μM 17-AAG for indicated durations. P53 DNA binding was determined by ChIP. (C) Diagram of cell-free luciferase fragment complementation assay that detects the DNA binding of p53-Cluc fusion protein. ZF-Nluc and p53-Cluc binding to DNA containing ZF and p53 sites juxtapose Nluc and Cluc domains to restore luciferase activity. (D) P53-Cluc and R282W-Cluc were pre-treated for 30 min at 34°C to inactivate R282W. The heat-treated p53-Cluc proteins were mixed with ZF-Nluc, DNA, ATP, E. coli extract containing 5 chaperones and incubated for 3 hrs at 23°C. P53 DNA binding was detected by measuring luciferase activity. The results are average of 3 experiments (mean ± SD). **p<0.01. (E) Coomassie staining of E. coli extract expressing molecular chaperones.
