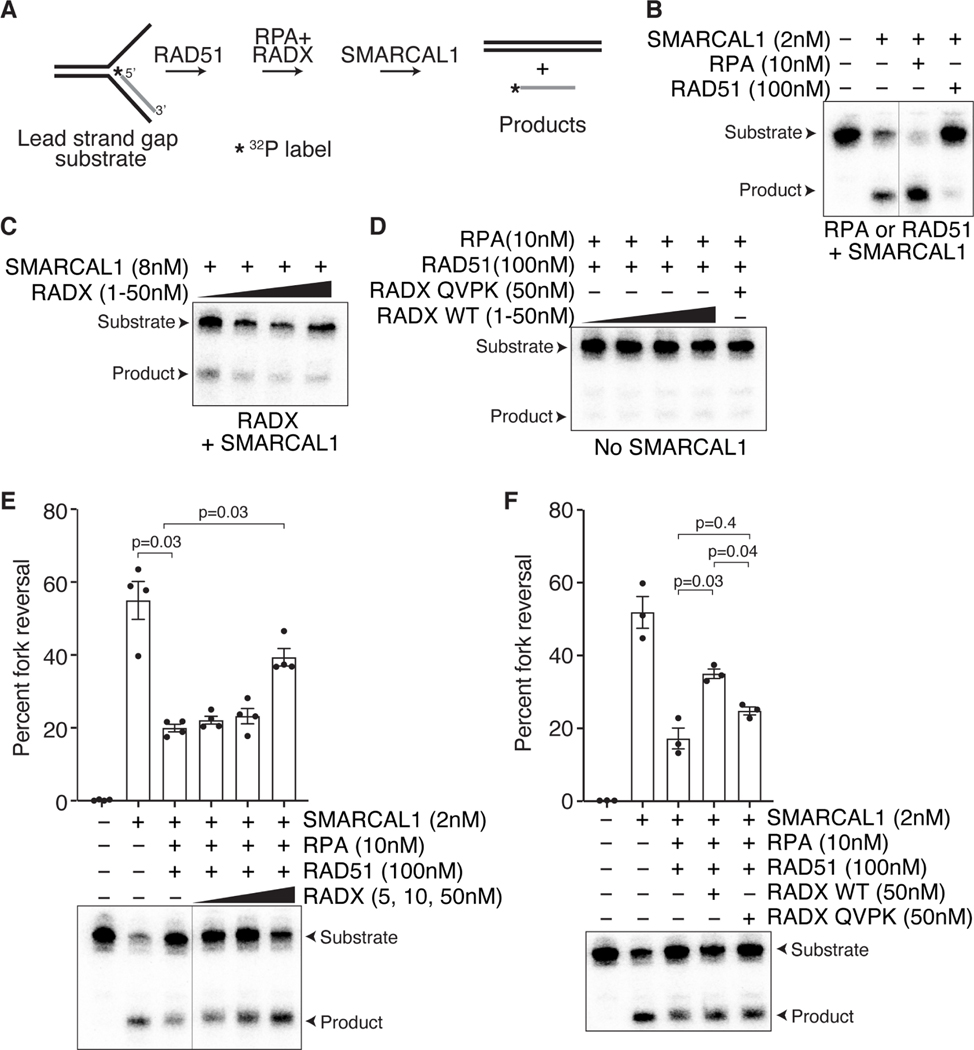
Figure 7. RADX promotes fork reversal by destabilizing RAD51 filaments in vitro.
(A) Schematic of the fork reversal assay. (B). Addition of RPA stimulates SMARCAL1- dependent fork reversal, while addition of RAD51 inhibits fork reversal. (C) Increasing concentrations of RADX by itself inhibits fork reversal by SMARCAL1. (D). Addition of RPA, RADX, and RAD51 do not catalyze fork reversal in the absence of SMARCAL1. (E) Addition of increasing concentrations of RADX in the presence of RPA overcomes the fork reversal inhibition caused by RAD51. Top, quantifications (n=4; mean+/−SEM). Bottom, representative experiment. (F) Unlike wild type RADX, RADX QVPK does not stimulate fork reversal in the presence of RAD51, RPA, and SMARCAL1. Top, quantifications (n=3; mean+/−SEM). A representative experiment is shown. A repeated measures one-way ANOVA with Sidaks multiple comparisons test was used to calculate p values. The line in blots indicate lanes were removed.