Figure 7.
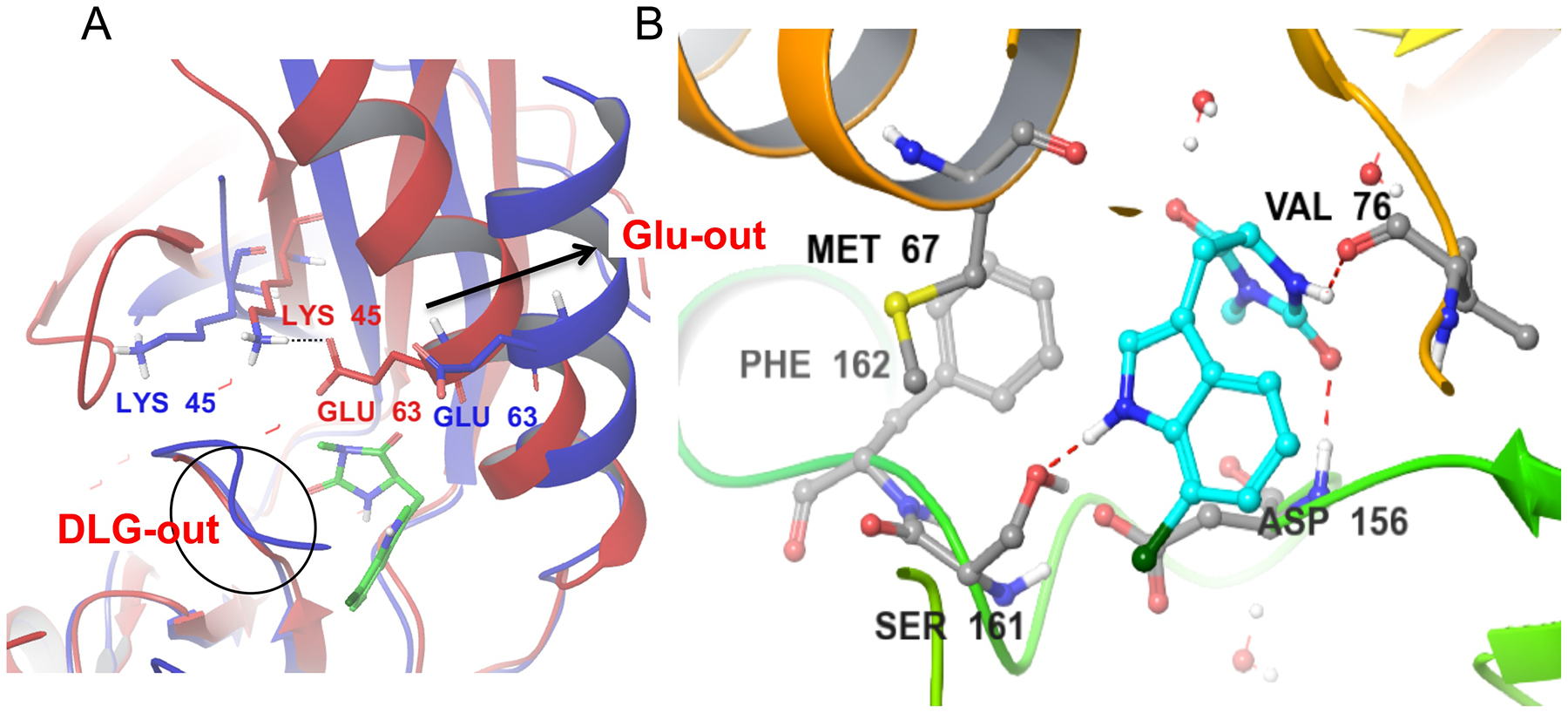
A) Alignment of the Nec-1s bound to RIPK1 in the DLG-out/Glu-out conformation (4ITH, blue) vs. the model of the active RIPK1 conformation, generated using homology modeling (red). Nec-1s binds exclusively in RIPK1 back pocket between activation segment and αC helix. This conformation is associated with the outward movement of the αC helix (arrow), breaking an ionic interaction of Glu63 with catalytic Lys45 and rotation of the DLG motif into the inactive conformation where the side-chain of Asp is not aligned with the ATP pocket. B) Binding of Nec-1s is mediated by three hydrogen bonds, including to the side chain of Ser161, an autophosphorylation site at the N-terminus of the activation loop. It is also stabilized by hydrophobic interactions, especially with the side-chains of Met67 in the αC helix and Phe162 in the activation loop.
