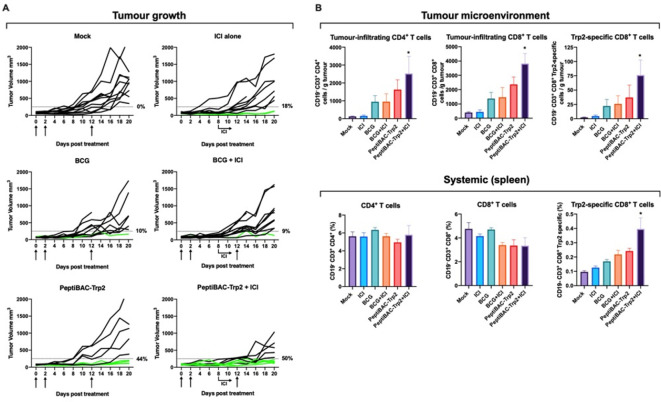
Figure 5.
PeptiBAC in combination with anti-PD1 improves tumor growth control compared with either monotherapy and induces robust infiltration of tumor-specific CD8+ T cells into tumors in a syngeneic mouse model of B16.F10.9/K1 melanoma. (A) Anti-PD-1 immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) alone (100 µg/dose given intraperitoneally three times a week, starting at day 8), BCG alone or in combination with anti-PD-1 ICI and PeptiBAC-Trp2 alone or in combination with anti-PD-1 ICI was given intratumorally 8, 10, and 22 days post tumor implantation. Individual tumor growth curves for all treatment groups are shown. A threshold of 250 mm3 was set to define the percentage of mice responding to the different therapies (dotted line). The percentage of responders in each treatment group is shown on the right side of the dotted line. (B) Immunological analysis of tumors and spleens of treated mice. The number of mice in each group was 9–11. Statistical analysis was performed with one-way analysis of variance. *p<0.05. PeptiBAC, peptide-coated Bacillus Calmette-Guérin; PD-1, programmed death 1.