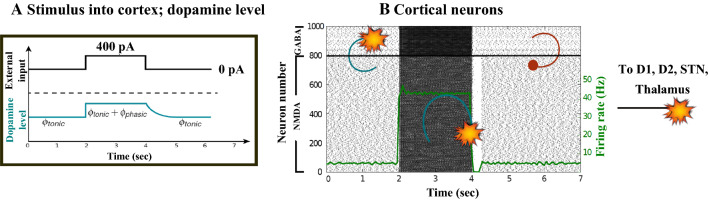
Fig. 12.
Healthy behaviour: adequate response to external stimulus with a high enough dopamine level ( and ) to make the BG direct pathway dominant. A External stimulus applied to the cortical neural populations (NMDA and GABA-receptor populations) and dopamine level, , increasing with cortical stimulation. B Raster plot of the spiking activity of the simulated populations of the cortical neurons when the action selection (direct) pathway is enabled by an adequate level of dopamine while an external stimulus is applied into the cortex. The NMDA-cortex population’s excitatory response is applied to the -MSNs, the -MSNs, the STN and the thalamus, and the result is given in Fig. 13. Each black dot corresponds to a spike of the corresponding neuron at a given time. The green function on the raster plot shows the average firing rate of the NMDA-cortical neurons for the 20 simulations produced. The raster plot is for one of these simulations. The sparks indicate excitatory connections, whereas the circles are inhibitory connections