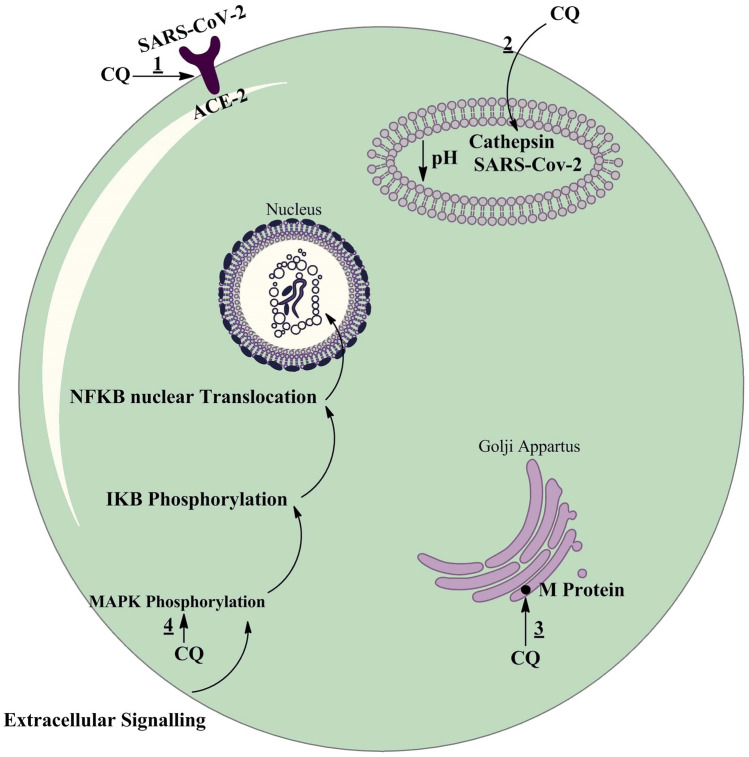
Fig. 1.
Possible effects of CQ on the SARS-CoV-2 replication cycle. (1) CQ interferes with glycosylation of ACE-2 receptor. Also it could limit the biosynthesis of sialic acids that may be required for cell surface binding of SARS-CoV-2. (2) CQ interferes with the pH-dependent-endosome-mediated viral entry of enveloped viruses through alkalization of endosome. So, it can inhibit fusion of the viral envelope and phospholipidic membrane of the endosomes resulting in release of the viral genome into the cell cytoplasm. (3) CQ interferes with post translational modification of viral proteins. CQ also interferes with proteolytic processing of the M protein (M protein is interacting with the other proteins of the virus, and plays an essential role during viral assembly) and alter virion assembly and budding. (4) CQ inhibits the activation (phosphorylation) of p38 MAPK. Also, it may inhibit virus replication