Figure 5: Ascites fluid-activated neutrophils damage T cells by trogocytosis of T-cell membranes.
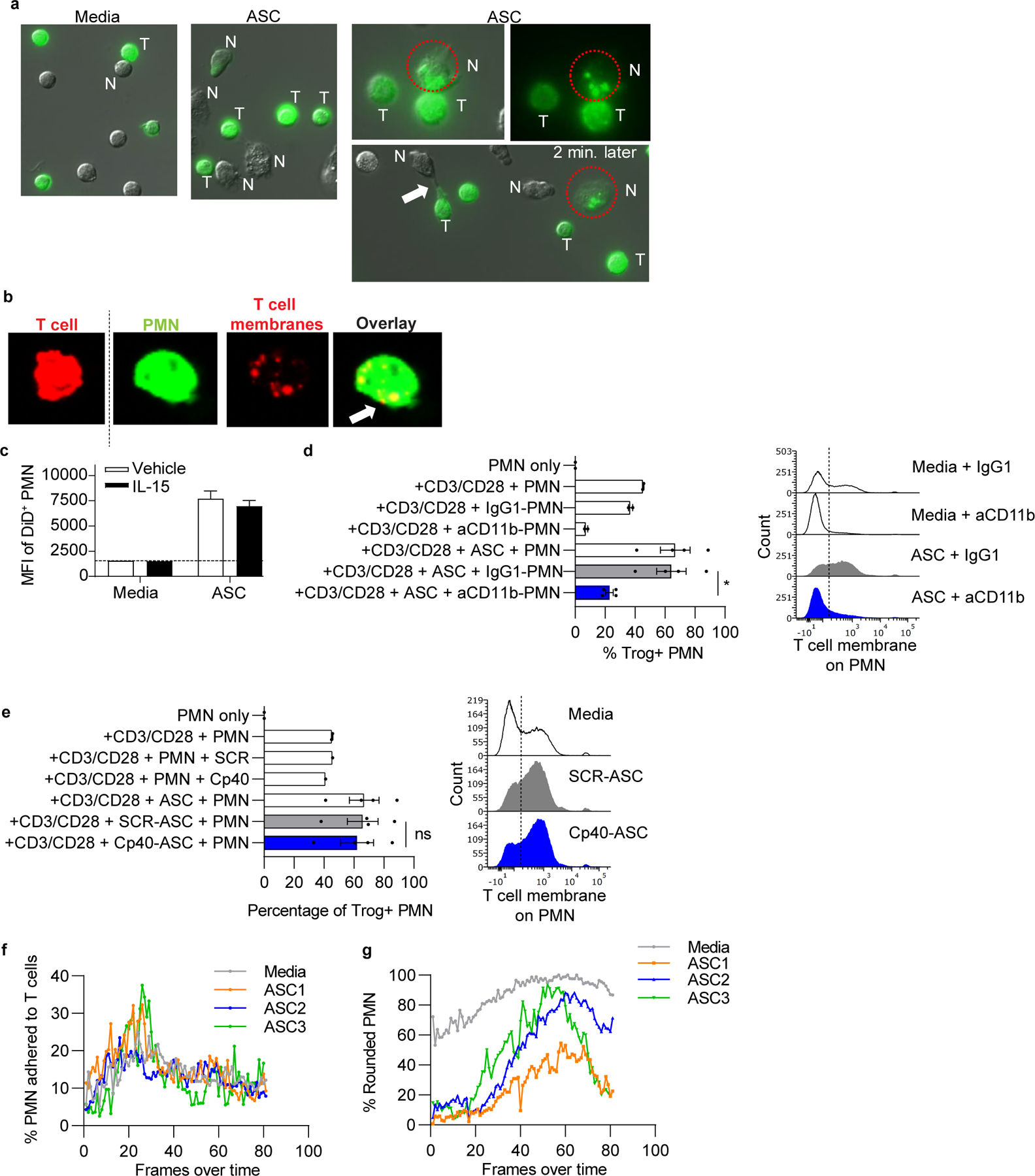
(a) Normal donor T cells were stained with a membrane dye, stimulated with anti-CD3/CD28 tetramers, and incubated with normal donor neutrophils and/or ASC. Cocultures were imaged by fluorescent microscopy over 3hrs. Representative images show cell contact and transfer of labeled T-cell membranes (green) to neutrophils in ASC cocultures. Circle shows neutrophil adherent to a T cell and containing T-cell membrane fragments, then separated from the T cell 2 minutes later. Arrow, neutrophil stretching T-cell membrane. N= neutrophil, T = T cell. (b) Anti-CD3/CD28 stimulated T cells (red) and neutrophils (green) were stained with membrane dyes, cocultured for 3hrs on glass coverslips, and analyzed by confocal microscopy. Representative images (left to right) of an intact T cell and a neutrophil with internalized T-cell membranes as demonstrated in the red channel and overlay image showing overlap of dyes (arrow). (c) ASC augments trogocytosis of T-cell membranes by neutrophils. T cells (n=3 normal donors) were stained with Vybrant DiD, stimulated with IL-15, and incubated with neutrophils in ASC (n=3) for 3hrs. Quantification of membrane transfer was assessed using MFI of Vybrant DiD on neutrophils. Results are from one experiment. (d,e) Neutrophil-mediated trogocytosis of T-cell membranes is dependent on CD11b, but independent of complement C3 activation. T cells and neutrophils were prepared and incubated as mentioned in panel a. Percent neutrophils with T-cell membrane (Trog+ neutrophils) was assessed by flow cytometry. Where indicated, neutrophils were pretreated with blocking anti-CD11b or isotype control (IgG1) (d) or ASC was pretreated with Cp40 (e). Symbols represent individual samples (n) and bars represent ± SEM. Statistical comparisons were by ANOVA with Tukey post hoc test (*p<0.05). (f,g) Percent neutrophils adhered to T cells was unaffected by ASC exposure. ASC induced elongation of neutrophils at early time points. Percent neutrophils adhered to T cells and neutrophil morphology following ASC exposure were quantified over time by live cell imaging. Neutrophil morphology was categorized as rounded or elongated, reflecting activation. Data are representative of two independent experiments unless otherwise noted.
