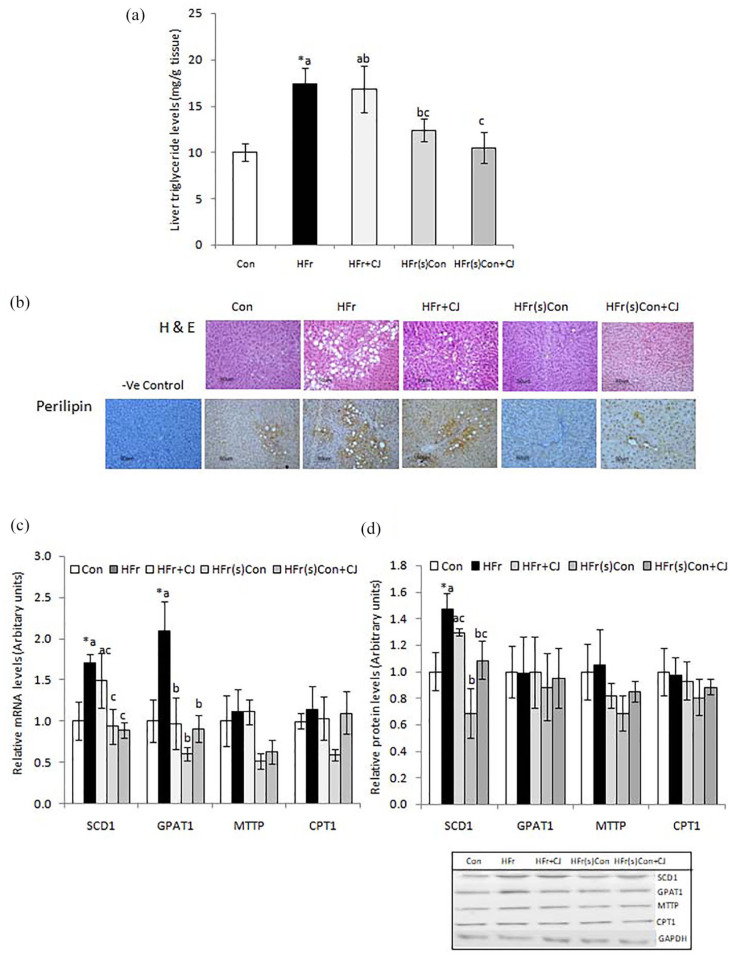
Figure 1.
Effect of carrot juice on tissue triglycerides, histology, and expression of lipid metabolic pathway genes and proteins. Values are expressed as means ± SE of 5 to 6 rats, except for gene and protein expression 4 rats from each group. (a) Liver triglycerides, (b) Representative photomicrographs of H and E stained liver sections and immunohistological staining of liver perilipin, a lipid droplet-associated protein (Top and Bottom, respectively) (20× magnification in Nikon-Eclipse E800 microscope), and (c and d) Hepatic lipid metabolic pathway mRNA and their protein levels with representative immunoblots. Data were analyzed by One way ANOVA with post hoc least significant difference test (post hoc LSD) and P ⩽ .05 level was considered significant. *Significant, when compared between control and HFr diet-fed groups. Bars bearing common superscripts are not different, otherwise, the bar bearing different superscripts is statistically different from others at P ⩽ .05 level.
Abbreviations: −ve, Negative; Con, Control diet; CPT1, Carnitine palmitoyl transferase 1; GPAT1, Glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase 1; HFr, High fructose diet; HFr + CJ, High fructose diet and carrot juice; HFr(s)Con, High fructose shifted to control diet; HFr(s)Con + CJ, High fructose shifted to control diet and carrot juice; MTTP, Microsomal triglyceride transfer protein; SCD1, Stearoyl-CoA desaturase 1.
Acidic ribosomal phosphoprotein (ARPP) and glyceraldehydes-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) were used for normalization of mRNA and protein expression respectively.