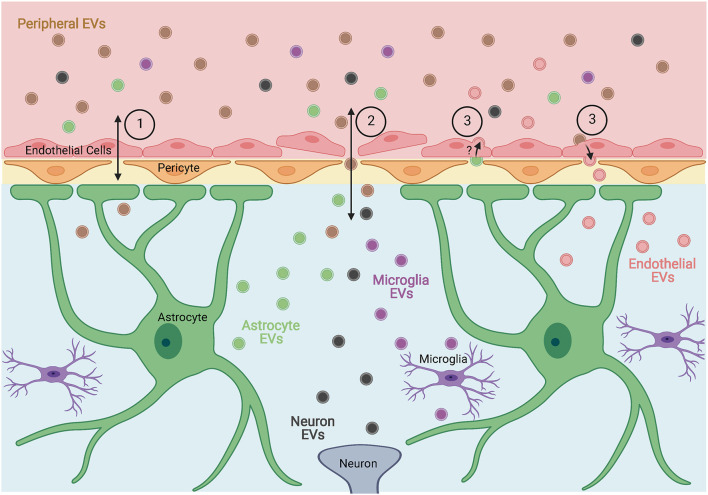
Figure 1.
Proposed mechanisms by which extracellular vesicles (EVs) cross the blood-brain barrier (BBB). EVs, or their contents, can enter or exit the brain through (1) receptor-mediated or adsorptive transcytosis, (2) breakdown of the BBB allowing for direct passage between endothelial cells, and (3) entry into endothelial cells and subsequent alteration of endothelial EVs. Figure created with BioRender.com.