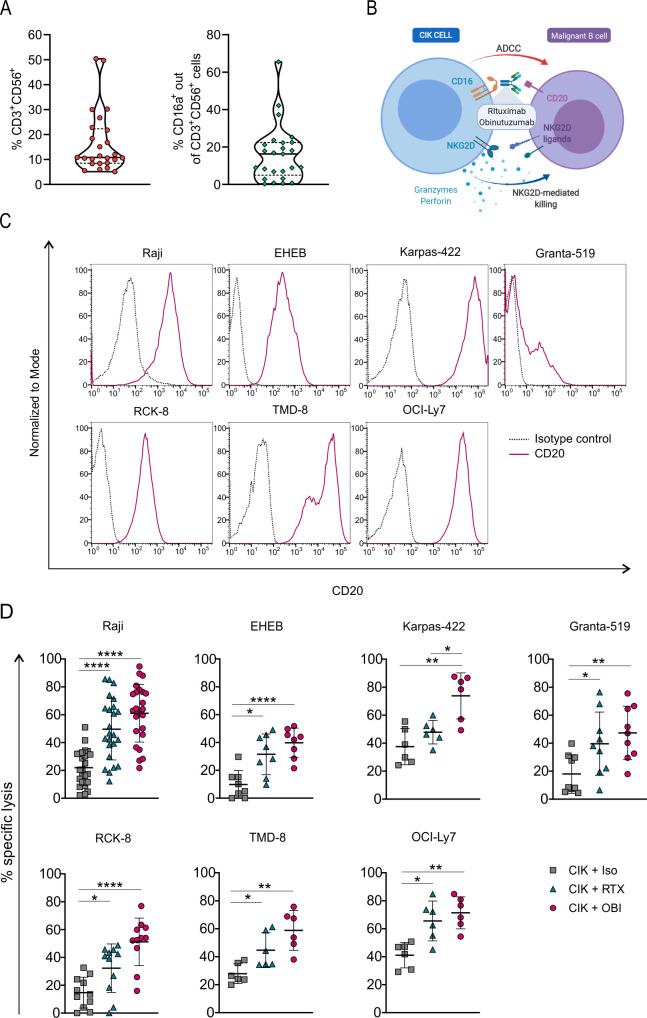
Figure 1.
CIK cell cytotoxicity is increased by the combination with anti-CD20 mAbs. (A) Violin plots showing 25th and 75th percentiles and median value of the percentage of CD3+ CD56+ CIK cells and CD16a+ CIK cell subsets within day 14 and 21 of cultures generated from healthy donors (n=25). (B) Graphical representation of the CIK+ mAbs combination strategy to target and kill B-cell malignancies (created with BioRender.com). (C) CD20 expression on Raji (Burkitt lymphoma), EHEB (EBV+ lymphoma), Karpas-422 (follicular lymphoma), Granta-519 (Mantle cell lymphoma), RCK-8, TMD-8, and OCI-Ly7 (diffuse large B-cell lymphoma) malignant B-cell lines. (D) Cytotoxicity of CIK cells in combination with an irrelevant antibody (CIK +Iso, squares) or with the anti-CD20 mAbs rituximab (CIK +RTX, triangles) or obinutuzumab (CIK +OBI, circles), against the B-cell tumor lines. Lytic activity was measured by a 4-hour calcein-AM release assay performed between days 14 and 21 of CIK cell cultures. The symbols refer to the specific killing of individual CIK cell cultures from different donors at an E/T ratio of 25:1, and mean values±SD (n=6–22) are reported. Data were analyzed by multiple t-test (*p<0.05, **p<0.01, and ****p<0.0001). ADCC, antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity; CIK, cytokine induced killer; mAbs, monoclonal antibodies; OBI, obinutuzumab; RTX, rituximab.